WoRMS taxon details
Gymnodinium catenatum H.W.Graham, 1943
109784 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:109784)
accepted
Species
marine, fresh, terrestrial
Graham H.1943. <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i>, a new dinoflagellate from the Gulf of California. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 62: 259-261. [details]
Type locality contained in Gulf of California
type locality contained in Gulf of California [details]
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46956
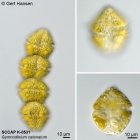
Description Chain-forming browngreen cells reaching up to 64 cells. Terminal cells are slightly wider than the others. Overall size:...
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46956 [details]
Description Chain-forming browngreen cells reaching up to 64 cells. Terminal cells are slightly wider than the others. Overall size:...
Description Chain-forming browngreen cells reaching up to 64 cells. Terminal cells are slightly wider than the others. Overall size: 48–65 μm in length and 30–43 μm wide (Fukuyo et al., 1990). Cingulum displaced on the left, cell surface covered with roughly hexagonal amphiesmal vesicles, horseshoe-shaped apical groove, numerous chloroplasts, nucleus large and centrally located. [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Gymnodinium catenatum H.W.Graham, 1943. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=109784 on 2025-04-08
Date
action
by
2006-07-25 11:42:39Z
changed
Camba Reu, Cibran
2015-06-26 12:00:51Z
changed
db_admin
Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
Nomenclature
original description
Graham H.1943. <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i>, a new dinoflagellate from the Gulf of California. Trans. Am. Microsc. Soc. 62: 259-261. [details]
basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details]
basis of record Gómez, F. (2005). A list of free-living dinoflagellate species in the world's oceans. <em>Acta Bot. Croat.</em> 64(1): 129-212. [details]
Ecology
ecology source
Jeong, H.; Yoo, Y.; Park, J.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 40: 133-150., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame040133 [details]
ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
Other
context source (Introduced species)
Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
context source (HKRMS) Clark, A. M. (1982). Echinoderms of Hong Kong. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Proceedings of the first international marine biological workshop: The marine flora and fauna of Hong Kong and southern China. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 1: 485-501. [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Brandt, S. (2001). Dinoflagellates, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 47-53 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., M.E. Cinar, M.A. Pancucci-Papadopoulou, J.G. Harmelin, G. Furnari, F. Andaloro, N. Bellou, N. Streftaris & H. Zibrowius. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Mee L.D., Espinosa M. & Diaz G. 1986. Paralytic shellfish poisoning with a <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i> red tide on the Pacific Coast of México. Mar. Env. Res. 19: 77-92. [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Balech, E. (1964). El Plancton de Mar del Plata durante el período 1961-1962 (Buenos Aires, Argentina). <em>Universidades Nacionales de Buenos Aires, La Plata y del Sur, P. E. de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Institute de Biologia Marina.</em> 4: 1-59. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
toxicology source Oshima Y., Hasegawa M., Yasumoto T., Hallegraeff G. & Blackburn S. 1987. Dinoflagellate <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i> as the source of paralytic shellfish toxins in Tasmanian shellfish. Toxicon 25: 1105-1111. [details]
toxicology source Anderson D.M., Sullivan J.J. & Reguera B. 1989. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in northwest Spain: the toxicity of the dinoflagellate <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i>. Toxicon 27: 665-674. [details]
context source (HKRMS) Clark, A. M. (1982). Echinoderms of Hong Kong. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Proceedings of the first international marine biological workshop: The marine flora and fauna of Hong Kong and southern China. Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 1: 485-501. [details]
additional source Streftaris, N., A. Zenetos & E. Papathanassiou. (2005). Globalisation in marine ecosystems: the story of non-indigenous marine species across European seas. <em>Oceanogry and Marine Biology: an Annual Review.</em> 43: 419-453. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Brandt, S. (2001). Dinoflagellates, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 47-53 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., M.E. Cinar, M.A. Pancucci-Papadopoulou, J.G. Harmelin, G. Furnari, F. Andaloro, N. Bellou, N. Streftaris & H. Zibrowius. (2005). Annotated list of marine alien species in the Mediterranean with records of the worst invasive species. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 6 (2): 63-118., available online at https://www.researchgate.net/publication/273213810_Annotated_list_of_marine_alien_species_in_the_Mediterranean_with_records_of_the_worst_invasive_species [details] Available for editors
additional source Mee L.D., Espinosa M. & Diaz G. 1986. Paralytic shellfish poisoning with a <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i> red tide on the Pacific Coast of México. Mar. Env. Res. 19: 77-92. [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Balech, E. (1964). El Plancton de Mar del Plata durante el período 1961-1962 (Buenos Aires, Argentina). <em>Universidades Nacionales de Buenos Aires, La Plata y del Sur, P. E. de la Provincia de Buenos Aires, Institute de Biologia Marina.</em> 4: 1-59. [details] Available for editors
toxicology source Oshima Y., Hasegawa M., Yasumoto T., Hallegraeff G. & Blackburn S. 1987. Dinoflagellate <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i> as the source of paralytic shellfish toxins in Tasmanian shellfish. Toxicon 25: 1105-1111. [details]
toxicology source Anderson D.M., Sullivan J.J. & Reguera B. 1989. Paralytic shellfish poisoning in northwest Spain: the toxicity of the dinoflagellate <i>Gymnodinium catenatum</i>. Toxicon 27: 665-674. [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46956 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Description Chain-forming browngreen cells reaching up to 64 cells. Terminal cells are slightly wider than the others. Overall size: 48–65 μm in length and 30–43 μm wide (Fukuyo et al., 1990). Cingulum displaced on the left, cell surface covered with roughly hexagonal amphiesmal vesicles, horseshoe-shaped apical groove, numerous chloroplasts, nucleus large and centrally located. [details]Harmful effect PSP producer. [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal Argentinean part of the South Atlantic Ocean (Marine Region) Ships: accidental with ballast water, sea water systems, live wells or other deck basins [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Spain (Nation) : Shipping [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Japanese | クサリハダカオビムシ | [details] |
Published in AlgaeBase 
To Barcode of Life (7 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Gymnodinium catenatum)
To GenBank (157413 nucleotides; 45450 proteins)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To ITIS

To Barcode of Life (7 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Gymnodinium catenatum)
To GenBank (157413 nucleotides; 45450 proteins)
To Global Invasive Species Database (GISD)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To ITIS