WoRMS taxon details
Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) F.Stein, 1878
110301 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:110301)
accepted
Species
Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860 · unaccepted (basionym)
Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella caspica Kiselev, 1940 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella cincta Schiller, 1918 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885 · unaccepted
Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881 · unaccepted (synonym)
Exuviaella ostenfeldi Schiller, 1933 · unaccepted (synonym)
Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994 · unaccepted (synonym)
Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976 · unaccepted
Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996 · unaccepted (synonym)
Xanthodiscus lauterbachii Schewiakoff, 1893 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, fresh, terrestrial
(of Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860) Ehrenberg C.G. 1860. Verzeichnis der Leuchtthierchen. Verhandl. Königl. Preuss. Akad. Wissensch. Berlin, Monatsberichte 1859: 791-793;
First figure (Fig. 2) given in Ehrenberg C.G. 1873. Die das Funkeln und Aufblitzen des Mittelmeeres bewirkenden kleinen Lebensformen. Gesellsch. Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin, Festschrift zur Feier des hundertjährigen Bestehens, 1-4. [details]
Type locality contained in Sorrento
type locality contained in Sorrento [details]
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46698
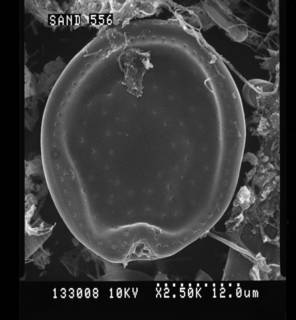
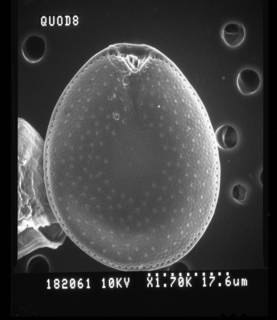
Description Almost round to oblong oval to ovoid cells with striking pyrenoid with starch sheath (visible as ring) in the centre of the...
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46698 [details]
Description Almost round to oblong oval to ovoid cells with striking pyrenoid with starch sheath (visible as ring) in the centre of the...
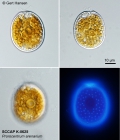
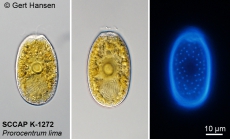
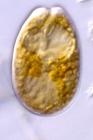
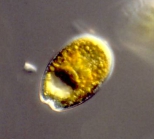
Description Almost round to oblong oval to ovoid cells with striking pyrenoid with starch sheath (visible as ring) in the centre of the cell. Ovoid is the most common cell shape. Smooth thecal surface with scattered large (round, ovoid, or kidneyshaped) pores and a marginal row of large (round or ovoid) pores. Plate centre devoid of pores. The periflagellar area is wide Vshaped, with collar and platelet lists adjacent to the pores in some cells. Eight platelets. The oval nucleus is posterior. [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Prorocentrum lima (Ehrenberg) F.Stein, 1878. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=110301 on 2025-04-18
Date
action
by
2015-06-26 12:00:51Z
changed
db_admin
Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
Nomenclature
original description
(of Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860) Ehrenberg C.G. 1860. Verzeichnis der Leuchtthierchen. Verhandl. Königl. Preuss. Akad. Wissensch. Berlin, Monatsberichte 1859: 791-793;
First figure (Fig. 2) given in Ehrenberg C.G. 1873. Die das Funkeln und Aufblitzen des Mittelmeeres bewirkenden kleinen Lebensformen. Gesellsch. Naturforschender Freunde zu Berlin, Festschrift zur Feier des hundertjährigen Bestehens, 1-4. [details]
original description (of Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994) Faust M.A. 1994. Three new benthic species of <i>Prorocentrum</i> (Dinophyceae) from Carrie Bow Cay, Belize: <i>P. sabulosum</i> sp. nov., <i>P. sculptile</i> sp. nov. and <i>P. arenarium</i> sp. nov. J. Phycol. 30: 755-763. [details]
original description (of Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994) Faust M.A. 1994. Three new benthic species of <i>Prorocentrum</i> (Dinophyceae) from Carrie Bow Cay, Belize: <i>P. sabulosum</i> sp. nov., <i>P. sculptile</i> sp. nov. and <i>P. arenarium</i> sp. nov. J. Phycol. 30: 755-763. [details]
Taxonomy
redescription
Nagahama, Y. & Fukuyo, Y. 2005. Redescription of <i>Cryptomonas lima</i>, collected from Sorrento, Italy, the basionym of <i>Prorocentrum lima</i>. Plankton Biol. Ecol. 52: 107-109. [details]
Ecology
ecology source
Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Faust, M.A. (1998). Mixotrophy in tropical benthic dinoflagellates. In: Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, L., Wyatt, T. (Eds.), Harmful Algae. Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae, Vigo, Spain, 1997, Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, France, pp. 390–393. [details]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Faust, M.A. (1998). Mixotrophy in tropical benthic dinoflagellates. In: Reguera, B., Blanco, J., Fernandez, L., Wyatt, T. (Eds.), Harmful Algae. Proceedings of the VIII International Conference on Harmful Algae, Vigo, Spain, 1997, Xunta de Galicia and Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission of UNESCO, Paris, France, pp. 390–393. [details]
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Brandt, S. (2001). Dinoflagellates, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 47-53 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Lakkis, S. (2011). Le phytoplancton marin du Liban (Méditerranée orientale): biologie, biodiversité, biogéographie. Aracne: Roma. ISBN 978-88-548-4243-4. 293 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S. A.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T. (2014). Marine benthic dinoflagellates - unravelling their worldwide biodiversity. <em>Kleine Senckenberg-Reihe.</em> 54: 1-276. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Steidinger, K.A. & Meave del Castillo, M.E. (Eds.). (2018). Guide to the identification of harmful micoalgae in the Gulf of Mexico. <em>St. Petersburg, FL: DiggyPOD, Inc.</em> [details]
additional source Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Zentz, F. (2019). A taxonomical study of benthic Prorocentrum species (Prorocentrales, Dinophyceae) from Anse Dufour (Martinique Island, eastern Caribbean Sea). <em>Marine Biodiversity.</em> 49(3): 1299-1319., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0913-6 [details]
additional source Hoppenrath, M.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T.; Schweikert, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Murray, S. (2013). Taxonomy and phylogeny of the benthic Prorocentrum species (Dinophyceae)—A proposal and review. <em>Harmful Algae.</em> 27: 1-28., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2013.03.006 [details]
toxicology source Murakami Y., Oshima Y. & Yasumoto T. 1982. Identification of okadaic acid as a toxic component of a marine dinoflagellate <i>Prorocentrum lima</i>. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 48: 69-72. [details]
toxicology source Tindall D.R., Dickey R.D., Carlson R.D. & Morey-Gaines G. 1984. Ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates from the Caribbean Sea. In: <i>Seafood Toxins</i> (Ed. by E.P. Ragelis), pp. 225-240. Am. Chem. Soc., Washington. [details]
toxicology source Torigoe K., Murata M. & Yasumoto T. 1988. Prorocentrolide, a toxic nitrogenous macrocycle from a marine dinoflagellate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110 : 7876-7877., available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00231a048 [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Tomas, C.R. (Ed.). (1997). Identifying marine phytoplankton. Academic Press: San Diego, CA [etc.] (USA). ISBN 0-12-693018-X. XV, 858 pp., available online at http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/book/9780126930184 [details]
additional source Brandt, S. (2001). Dinoflagellates, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 47-53 (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Lakkis, S. (2011). Le phytoplancton marin du Liban (Méditerranée orientale): biologie, biodiversité, biogéographie. Aracne: Roma. ISBN 978-88-548-4243-4. 293 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Hoppenrath, M.; Murray, S. A.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T. (2014). Marine benthic dinoflagellates - unravelling their worldwide biodiversity. <em>Kleine Senckenberg-Reihe.</em> 54: 1-276. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Steidinger, K.A. & Meave del Castillo, M.E. (Eds.). (2018). Guide to the identification of harmful micoalgae in the Gulf of Mexico. <em>St. Petersburg, FL: DiggyPOD, Inc.</em> [details]
additional source Chomérat, N.; Bilien, G.; Zentz, F. (2019). A taxonomical study of benthic Prorocentrum species (Prorocentrales, Dinophyceae) from Anse Dufour (Martinique Island, eastern Caribbean Sea). <em>Marine Biodiversity.</em> 49(3): 1299-1319., available online at https://doi.org/10.1007/s12526-018-0913-6 [details]
additional source Hoppenrath, M.; Chomérat, N.; Horiguchi, T.; Schweikert, M.; Nagahama, Y.; Murray, S. (2013). Taxonomy and phylogeny of the benthic Prorocentrum species (Dinophyceae)—A proposal and review. <em>Harmful Algae.</em> 27: 1-28., available online at https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hal.2013.03.006 [details]
toxicology source Murakami Y., Oshima Y. & Yasumoto T. 1982. Identification of okadaic acid as a toxic component of a marine dinoflagellate <i>Prorocentrum lima</i>. Bull. Jap. Soc. Sci. Fish. 48: 69-72. [details]
toxicology source Tindall D.R., Dickey R.D., Carlson R.D. & Morey-Gaines G. 1984. Ciguatoxigenic dinoflagellates from the Caribbean Sea. In: <i>Seafood Toxins</i> (Ed. by E.P. Ragelis), pp. 225-240. Am. Chem. Soc., Washington. [details]
toxicology source Torigoe K., Murata M. & Yasumoto T. 1988. Prorocentrolide, a toxic nitrogenous macrocycle from a marine dinoflagellate. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 110 : 7876-7877., available online at https://doi.org/10.1021/ja00231a048 [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Nontype (of Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994) SCCAP K-0625 [details]
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:46698 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Description Almost round to oblong oval to ovoid cells with striking pyrenoid with starch sheath (visible as ring) in the centre of the cell. Ovoid is the most common cell shape. Smooth thecal surface with scattered large (round, ovoid, or kidneyshaped) pores and a marginal row of large (round or ovoid) pores. Plate centre devoid of pores. The periflagellar area is wide Vshaped, with collar and platelet lists adjacent to the pores in some cells. Eight platelets. The oval nucleus is posterior. [details]Harmful effect Prorocentrum lima has been found to produce the Diarrhetic Shellfish Poisoning (DSP) toxins: okadaic acid (Murakami et al. 1982), DTX-1 (Lee et al. 1989), DTX-2 (Hu et al. 1993), in addition to a prorocentrolide (Torigoe et al. 1988) and a Fast Acting Toxin (FAT) (Tindall et al. 1984). [details]
Identification Similar species: P. consutum, P. maculosum. Remarks: A wide range of morphological variability has been reported for P. lima. It appears to contain cryptic diversity and the proposal by Aligizaki et al. (2009) to refer to it as the “P. lima complex” should be followed.
For morphological identification help look here: https://www.dinophyta.org/identification-keys/marine-benthic-dinoflagellates/prorocentrum-ident-spp-pages/
or check out this key: https://keys.lucidcentral.org/keys/v4/prorocentrum/ [details]
Synonymy Various taxa have been regarded by various authors as taxonomical synonyms of P. lima, e.g, Exuviaella marina Cienkowski 1881; Dinopyxis laevis Stein 1883, Exuviaella chathamensis Lemmermann 1907; Exuviaella cincta Schiller 1918; Exuviaella ostenfeldii Schiller 1931; Exuviaella caspica Kisselev 1940 and their respective nomenclatural synonyms. Note that several papers in which P. lima or one of the synonyms have been used, do not deal with this species, concluded on the figures included. [details]
Published in AlgaeBase 
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
(from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)
(from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
(from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
(from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)
(from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)
(from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)
(from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)
(from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)
(from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella cincta Schiller, 1918)
(from synonym Exuviaella cincta Schiller, 1918)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella ostenfeldi Schiller, 1933)
(from synonym Exuviaella ostenfeldi Schiller, 1933)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Exuviaella caspica Kiselev, 1940)
(from synonym Exuviaella caspica Kiselev, 1940)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Xanthodiscus lauterbachii Schewiakoff, 1893)
(from synonym Xanthodiscus lauterbachii Schewiakoff, 1893)
To Barcode of Life (32 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (17 publications) (from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (38 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Prorocentrum arenarium) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Prorocentrum lima)
To GenBank (10 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins) (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins) (from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins)
To NMNH Extant Collection (133008.jpg) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To NMNH Extant Collection (133008C.jpg) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To NMNH Extant Collection (182059.jpg)
To NMNH Extant Collection (182061.jpg)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
To ITIS

Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
(from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)
(from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
(from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
(from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)
(from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)
(from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)
(from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)
(from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)
(from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella cincta Schiller, 1918)
(from synonym Exuviaella cincta Schiller, 1918)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella ostenfeldi Schiller, 1933)
(from synonym Exuviaella ostenfeldi Schiller, 1933)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Exuviaella caspica Kiselev, 1940)
(from synonym Exuviaella caspica Kiselev, 1940)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Xanthodiscus lauterbachii Schewiakoff, 1893)
(from synonym Xanthodiscus lauterbachii Schewiakoff, 1893)To Barcode of Life (32 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) F.Schütt, 1896)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (12 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella lima (Ehrenberg) Bütschli, 1885)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (17 publications) (from synonym Dinopyxis laevis F.Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) A.R.Loeblich, 1976)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (3 publications) (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (38 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella marina Cienkowski, 1881)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Exuviaella laevis (Stein) Schroder, 1900)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Prorocentrum arenarium) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Prorocentrum lima)
To GenBank (10 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins) (from synonym Cryptomonas lima Ehrenberg, 1860)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins) (from synonym Exuviaella marina var. lima (Ehrenberg) Schiller, 1931)
To GenBank (386 nucleotides; 52 proteins)
To NMNH Extant Collection (133008.jpg) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To NMNH Extant Collection (133008C.jpg) (from synonym Prorocentrum arenarium M.A.Faust, 1994)
To NMNH Extant Collection (182059.jpg)
To NMNH Extant Collection (182061.jpg)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Prorocentrum marinum (Cienkowski) Steidinger & Williams ex Head, 1996)
To ITIS