WoRMS taxon details
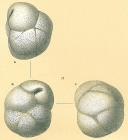
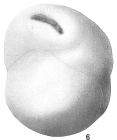
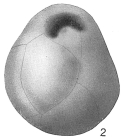
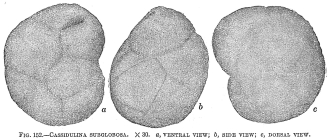
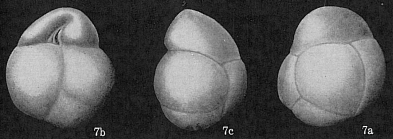
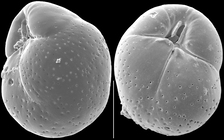
Globocassidulina subglobosa (Brady, 1881)
113091 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:113091)
accepted
Species
Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881 · unaccepted (Type species of Globocassidulina)
Globocassidulina mucronata Nomura, 1983 · unaccepted (junior synonym opinion of Scott (2000))
Islandiella subglobosa (Brady, 1881) · unaccepted
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
recent + fossil
(of Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881) Brady, H. B. (1881). Notes on some of the Reticularian Rhizopoda of the "Challenger" Expedition. Part III. <em>Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science.</em> (2) 21 (81): 31-71., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13808725
page(s): p. 60, illustrated in Brady, 1884, pl. 54, fig. 17 [details]
page(s): p. 60, illustrated in Brady, 1884, pl. 54, fig. 17 [details]
Hayward, B.W.; Le Coze, F.; Vachard, D.; Gross, O. (2025). World Foraminifera Database. Globocassidulina subglobosa (Brady, 1881). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=113091 on 2025-04-05
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
(of Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881) Brady, H. B. (1881). Notes on some of the Reticularian Rhizopoda of the "Challenger" Expedition. Part III. <em>Quarterly Journal of Microscopical Science.</em> (2) 21 (81): 31-71., available online at https://biodiversitylibrary.org/page/13808725
page(s): p. 60, illustrated in Brady, 1884, pl. 54, fig. 17 [details]
original description (of Globocassidulina mucronata Nomura, 1983) Nomura, R. (1983). Cassidulinidae (foraminiferida) from the uppermost Cenozoic of Japan (part 1). <em>Tohoku University Scientific Reports, 2nd Series (Geology).</em> 53:1-101, pls. 1-25., available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10097/00104991
page(s): p. 63, pl. 1, figures 12 and 13; pl. 13, figures 2-4). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
basis of record Gross, O. (2001). Foraminifera, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 60-75 (look up in IMIS) [details]
page(s): p. 60, illustrated in Brady, 1884, pl. 54, fig. 17 [details]
original description (of Globocassidulina mucronata Nomura, 1983) Nomura, R. (1983). Cassidulinidae (foraminiferida) from the uppermost Cenozoic of Japan (part 1). <em>Tohoku University Scientific Reports, 2nd Series (Geology).</em> 53:1-101, pls. 1-25., available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10097/00104991
page(s): p. 63, pl. 1, figures 12 and 13; pl. 13, figures 2-4). [details] Available for editors
basis of record Gross, O. (2001). Foraminifera, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 60-75 (look up in IMIS) [details]
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (HKRMS) Yim, W. W.-S.; He, X.-X. (1988). Holocene foraminifera in Hong Kong and their palaeoenvironmental significance. <em>In: The palaeoenvironment of east asia from the mid-tertiary, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Paleoenvironment of East Asia, Vol. II: Oceanography, Palaeozoology and Palaeoanthropology (eds. Whyte, P. Aigner, J.S., Jablonski, N.G., Taylor, G., Walker, D., Pinxian, W. & So, C.-L.), Centre of Asian Studies, University of Hong Kong.</em> 787-809. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (WoRCS) Romano, E.; Bergamin, L.; Di Bella, L.; Frezza, V.; Marassich, A.; Pierfranceschi, G.; Provenzani, C. (2020). Benthic foraminifera as proxies of marine influence in the Orosei marine caves, Sardinia, Italy. <em>Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems.</em> 30: 701–716., available online at https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3288 [details]
additional source Murray, J.W. & Pudsey, C.J. (2004). Living (stained) and dead foraminifera from the newly ice-free Larsen Ice Shelf, Weddell Sea, Antarctica: ecology and taphonomy. <em>Marine Micropaleontology.</em> 53: 67-81. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Cornelius, N.; Gooday, A. J. (2004). ‘Live'(stained) deep-sea benthic foraminiferans in the western Weddell Sea: trends in abundance, diversity, and taxonomic composition along a depth transect. <em>Deep-Sea Research II.</em> 51: 1571-1602. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Sen Gupta, B. K.; Smith, L. E.; Machain-Castillo, M. L. (2009). Foraminifera of the Gulf of Mexico in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas.</em> 87-129. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Rupp, C.; Haunold-Jenke, Y. (2003). Untermiozäne Foraminiferenfaunen aus dem oberösterreichischen Zentralraum - Lower Miocene Foraminifera faunas from central upper Austria. <em>Jahrbuch der geologischen Bundesanstalt.</em> 143(2): 227-302., available online at https://opac.geologie.ac.at/wwwopacx/wwwopac.ashx?command=getcontent&server=images&value=JB1432_227_A.pdf [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (HKRMS) Yim, W. W.-S.; He, X.-X. (1988). Holocene foraminifera in Hong Kong and their palaeoenvironmental significance. <em>In: The palaeoenvironment of east asia from the mid-tertiary, Proceedings of the Second International Conference on the Paleoenvironment of East Asia, Vol. II: Oceanography, Palaeozoology and Palaeoanthropology (eds. Whyte, P. Aigner, J.S., Jablonski, N.G., Taylor, G., Walker, D., Pinxian, W. & So, C.-L.), Centre of Asian Studies, University of Hong Kong.</em> 787-809. [details] Available for editors
context source (WoRCS) Romano, E.; Bergamin, L.; Di Bella, L.; Frezza, V.; Marassich, A.; Pierfranceschi, G.; Provenzani, C. (2020). Benthic foraminifera as proxies of marine influence in the Orosei marine caves, Sardinia, Italy. <em>Aquatic Conservation: Marine and Freshwater Ecosystems.</em> 30: 701–716., available online at https://doi.org/10.1002/aqc.3288 [details]
additional source Murray, J.W. & Pudsey, C.J. (2004). Living (stained) and dead foraminifera from the newly ice-free Larsen Ice Shelf, Weddell Sea, Antarctica: ecology and taphonomy. <em>Marine Micropaleontology.</em> 53: 67-81. [details] Available for editors
additional source Cornelius, N.; Gooday, A. J. (2004). ‘Live'(stained) deep-sea benthic foraminiferans in the western Weddell Sea: trends in abundance, diversity, and taxonomic composition along a depth transect. <em>Deep-Sea Research II.</em> 51: 1571-1602. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sen Gupta, B. K.; Smith, L. E.; Machain-Castillo, M. L. (2009). Foraminifera of the Gulf of Mexico in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas.</em> 87-129. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Rupp, C.; Haunold-Jenke, Y. (2003). Untermiozäne Foraminiferenfaunen aus dem oberösterreichischen Zentralraum - Lower Miocene Foraminifera faunas from central upper Austria. <em>Jahrbuch der geologischen Bundesanstalt.</em> 143(2): 227-302., available online at https://opac.geologie.ac.at/wwwopacx/wwwopac.ashx?command=getcontent&server=images&value=JB1432_227_A.pdf [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Unreviewed
Habitat Known from seamounts and knolls [details]
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (59 publications) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Globocassidulina subglobosa)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To NMNH Paleobiology Collection (Cassidulina subglobosa USNM MO 625092) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To PESI (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To PESI
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (59 publications) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Globocassidulina subglobosa)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To NMNH Paleobiology Collection (Cassidulina subglobosa USNM MO 625092) (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To PESI (from synonym Cassidulina subglobosa Brady, 1881)
To PESI