WoRMS taxon details
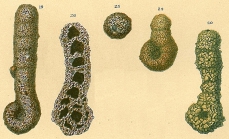
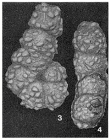
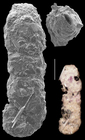
Ammobaculites agglutinans (d'Orbigny, 1846)
114024 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:114024)
accepted
Species
Haplophragmium agglutinans (d'Orbigny, 1846) · unaccepted
Spirolina agglutinans d'Orbigny, 1846 · unaccepted (Type species of Ammobaculites)
marine, fresh, terrestrial
recent + fossil
(of Spirolina agglutinans d'Orbigny, 1846) Orbigny, A. D. d'. (1846). Die fossilen Foraminiferen des tertiären Beckens von Wien. Foraminifères fossiles du bassin tertiaire de Vienne. 312 p., available online at https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_JKpAAAAAcAAJ
page(s): p. 137, pl. 7, figs. 10–12. [details]
page(s): p. 137, pl. 7, figs. 10–12. [details]
Hayward, B.W.; Le Coze, F.; Vachard, D.; Gross, O. (2025). World Foraminifera Database. Ammobaculites agglutinans (d'Orbigny, 1846). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=114024 on 2025-04-04
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
(of Spirolina agglutinans d'Orbigny, 1846) Orbigny, A. D. d'. (1846). Die fossilen Foraminiferen des tertiären Beckens von Wien. Foraminifères fossiles du bassin tertiaire de Vienne. 312 p., available online at https://archive.org/details/bub_gb_JKpAAAAAcAAJ
page(s): p. 137, pl. 7, figs. 10–12. [details]
basis of record Gross, O. (2001). Foraminifera, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 60-75 (look up in IMIS) [details]
new combination reference Bartenstein, H. (1952). Taxonomische Bemerkungen zu den Ammobaculites, Haplophragmium, Lituola und verwandten Gattungen (For.). <em>Senckenbergiana.</em> 33: 313-342.
page(s): p. 318, pl. 1, fig. 1; pl. 2, figs. 10–16. [details]
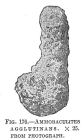
new combination reference Cushman, J. A. (1910). A monograph of the Foraminifera of the North Pacific Ocean. Part I. Astrorhizidae and Lituolidae. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 71(1): 1-134., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/7878332
page(s): p. 115, Fig. 176 [details]
page(s): p. 137, pl. 7, figs. 10–12. [details]
basis of record Gross, O. (2001). Foraminifera, <B><I>in</I></B>: Costello, M.J. <i>et al.</i> (Ed.) (2001). <i>European register of marine species: a check-list of the marine species in Europe and a bibliography of guides to their identification. Collection Patrimoines Naturels,</i> 50: pp. 60-75 (look up in IMIS) [details]
new combination reference Bartenstein, H. (1952). Taxonomische Bemerkungen zu den Ammobaculites, Haplophragmium, Lituola und verwandten Gattungen (For.). <em>Senckenbergiana.</em> 33: 313-342.
page(s): p. 318, pl. 1, fig. 1; pl. 2, figs. 10–16. [details]
new combination reference Cushman, J. A. (1910). A monograph of the Foraminifera of the North Pacific Ocean. Part I. Astrorhizidae and Lituolidae. <em>Bulletin of the United States National Museum.</em> 71(1): 1-134., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/7878332
page(s): p. 115, Fig. 176 [details]
Other
context source (Deepsea)
Intergovernmental Oceanographic Commission (IOC) of UNESCO. The Ocean Biogeographic Information System (OBIS), available online at http://www.iobis.org/ [details]
context source (Bermuda) Javaux, E. J. J. M. (1999). Benthic foraminifera from the modern sediments of Bermuda Implications for Holocene sea-level Studies. Ph.D. dissertation - Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 1-387, available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10222/75105 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Cornelius, N.; Gooday, A. J. (2004). ‘Live'(stained) deep-sea benthic foraminiferans in the western Weddell Sea: trends in abundance, diversity, and taxonomic composition along a depth transect. <em>Deep-Sea Research II.</em> 51: 1571-1602. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Sen Gupta, B. K.; Smith, L. E.; Machain-Castillo, M. L. (2009). Foraminifera of the Gulf of Mexico in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas.</em> 87-129. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
context source (Bermuda) Javaux, E. J. J. M. (1999). Benthic foraminifera from the modern sediments of Bermuda Implications for Holocene sea-level Studies. Ph.D. dissertation - Dalhousie University, Halifax, Nova Scotia, 1-387, available online at http://hdl.handle.net/10222/75105 [details] Available for editors
additional source Cornelius, N.; Gooday, A. J. (2004). ‘Live'(stained) deep-sea benthic foraminiferans in the western Weddell Sea: trends in abundance, diversity, and taxonomic composition along a depth transect. <em>Deep-Sea Research II.</em> 51: 1571-1602. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sen Gupta, B. K.; Smith, L. E.; Machain-Castillo, M. L. (2009). Foraminifera of the Gulf of Mexico in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. <em>Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College Station, Texas.</em> 87-129. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Unreviewed
Habitat Known from seamounts and knolls [details]