WoRMS taxon details
Scrippsiella acuminata (Ehrenberg) Kretschmann, Elbrächter, Zinssmeister, S.Soehner, Kirsch, Kusber & Gottschling, 2015
1321853 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:1321853)
accepted
Species
Calciodinellum faeroense (Paulsen) Havskum, 1991 · unaccepted (synonym)
Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899 · unaccepted (synonym)
Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883 · unaccepted (synonym)
Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883 · unaccepted
Goniodoma lacustris Lindemann, 1924 · unaccepted (synonym)
Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836 · unaccepted (synonym)
Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905 · unaccepted (synonym)
Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910 · unaccepted (synonym)
Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967 · unaccepted (synonym)
Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966 · unaccepted (synonym)
Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine
Not documented
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Scrippsiella acuminata (Ehrenberg) Kretschmann, Elbrächter, Zinssmeister, S.Soehner, Kirsch, Kusber & Gottschling, 2015. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=1321853 on 2025-04-15
Date
action
by
Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
Nomenclature
basis of record
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
new combination reference Kretschmann, J.; Elbrächter, M.; Zinssmeister, C.; Soehner, S.; Kirsch, M.; Kusber, W.-H.; Gottschling, M. (2015). Taxonomic clarification of the dinophyte Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenb., ≡ Scrippsiella acuminata, comb. nov. (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales). <em>Phytotaxa.</em> 220(3): 239., available online at https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.220.3.3 [details]
new combination reference Kretschmann, J.; Elbrächter, M.; Zinssmeister, C.; Soehner, S.; Kirsch, M.; Kusber, W.-H.; Gottschling, M. (2015). Taxonomic clarification of the dinophyte Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenb., ≡ Scrippsiella acuminata, comb. nov. (Thoracosphaeraceae, Peridiniales). <em>Phytotaxa.</em> 220(3): 239., available online at https://doi.org/10.11646/phytotaxa.220.3.3 [details]
Ecology
ecology source
Hansen, P. J.; Tillmann, U. (2020). Mixotrophy in Dinoflagellates: Prey Selection, Physiology and Ecological Importance in Dinoflagellates: Classification, Evolution, Physiology and Ecological Significance. <em>Ed: Subba Rao Durvasula. Publisher: Nova Science Publishers, Inc. New York, USA.</em> [details]
ecology source Jeong, H.; Yoo, Y.; Park, J.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 40: 133-150., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame040133 [details]
ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Jeong, H.; Park, J.; Nho, J.; Park, M.; Ha, J.; Seong, K.; Jeng, C.; Seong, C.; Lee, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by red-tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 41: 131-143., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame041131 [details]
ecology source Jeong, H.; Yoo, Y.; Park, J.; Song, J.; Kim, S.; Lee, S.; Kim, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by phototrophic red-tide dinoflagellates: five species newly revealed and six species previously known to be mixotrophic. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 40: 133-150., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame040133 [details]
ecology source Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Jeong, H.; Park, J.; Nho, J.; Park, M.; Ha, J.; Seong, K.; Jeng, C.; Seong, C.; Lee, K.; Yih, W. (2005). Feeding by red-tide dinoflagellates on the cyanobacterium Synechococcus. <em>Aquatic Microbial Ecology.</em> 41: 131-143., available online at https://doi.org/10.3354/ame041131 [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From regional or thematic species database
Harmful effect Non-toxigenic marine microalgal species associated with animal kills or health impairment. [details]
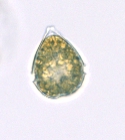
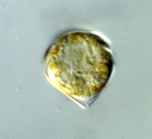
PlanktonNet Image (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
(from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)
(from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
(from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)
(from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)
(from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Calciodinellum faeroense (Paulsen) Havskum, 1991)
(from synonym Calciodinellum faeroense (Paulsen) Havskum, 1991)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Heteraulacus acuminatus (Ehrenberg, 1836) Diesing, 1850)
(from synonym Heteraulacus acuminatus (Ehrenberg, 1836) Diesing, 1850)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)
(from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)
(from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)
Published in AlgaeBase
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Goniodoma lacustris Lindemann, 1924)
(from synonym Goniodoma lacustris Lindemann, 1924)
To Barcode of Life (8 barcodes) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (20 publications) (from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (26 publications) (from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (49 publications) (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (55 publications) (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (9 publications) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Dyntaxa (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Dyntaxa (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Scrippsiella acuminata)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Scrippsiella trochoidea) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To GenBank (170 nucleotides; 27 proteins) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To GenBank (170 nucleotides; 27 proteins) (from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)
To GenBank (65 nucleotides; 1 proteins)
To GenBank (65 nucleotides; 1 proteins) (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
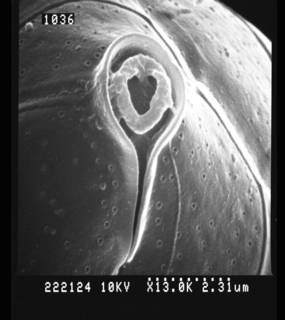
To NMNH Extant Collection (222124.jpg) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To NMNH Extant Collection (222177.jpg) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To PESI (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)
Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
(from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)
(from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
(from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)
(from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)
(from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)
(from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Calciodinellum faeroense (Paulsen) Havskum, 1991)
(from synonym Calciodinellum faeroense (Paulsen) Havskum, 1991)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Heteraulacus acuminatus (Ehrenberg, 1836) Diesing, 1850)
(from synonym Heteraulacus acuminatus (Ehrenberg, 1836) Diesing, 1850)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)
(from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)
(from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)Published in AlgaeBase

Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Goniodoma lacustris Lindemann, 1924)
(from synonym Goniodoma lacustris Lindemann, 1924)To Barcode of Life (8 barcodes) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (10 publications) (from synonym Glenodinium acuminatum (Ehrenberg) E.Jörgensen, 1899)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (20 publications) (from synonym Peridinium trochoideum (F.Stein) Lemmermann, 1910)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (26 publications) (from synonym Glenodinium trochoideum F.Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (49 publications) (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (55 publications) (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Peridinium faeroense O.W.Paulsen, 1905)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (9 publications) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Dyntaxa (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To Dyntaxa (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Scrippsiella acuminata)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Scrippsiella trochoidea) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To GenBank (170 nucleotides; 27 proteins) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To GenBank (170 nucleotides; 27 proteins) (from synonym Scrippsiella faeronese Dickensheets & Cox, 1971)
To GenBank (65 nucleotides; 1 proteins)
To GenBank (65 nucleotides; 1 proteins) (from synonym Peridinium acuminatum Ehrenberg, 1836)
To Global Biotic Interactions (GloBI) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To NMNH Extant Collection (222124.jpg) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To NMNH Extant Collection (222177.jpg) (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella trochoidea (F.Stein) A.R.Loeblich III, 1976)
To PESI (from synonym Goniodoma acuminatum (Ehrenberg) Stein, 1883)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroense (Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1967)
To PESI (from synonym Scrippsiella faeroensis (O.W.Paulsen) Balech & Soares, 1966)