WoRMS taxon details
Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786)
207449 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:207449)
accepted
Species
Astraea (Favastraea) magnifica de Blainville, 1834 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Astraea (Fissicella) filicosa Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) fuscoviridis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) magnifica Blainville, 1834 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) magnifica (de Blainville, 1834) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) robusta Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea (Fissicella) virens Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Astraea filicosa Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea fuscoviridis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea magnifica Blainville, 1830 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea robusta Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astraea virens Dana, 1846 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea filicosa (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea fuscoviridis Quoy & Gaimard, 1833 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea hemprichii (Ehrenberg, 1834) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea magnifica Blainville, 1830 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Astrea virens (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favastrea magnifica (Blainville, 1830) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Favia crassior (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favia hemprichii (Ehrenberg, 1834) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favia robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. fuscovirides (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. magnifica (Blainville, 1830) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. profundicella (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. quoyi (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites abdita var. virens (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites astrinus Link, 1807 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites crassior (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites filicosa (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites fuscoviridis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites gibbosa (Klunzinger, 1879) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites magnifica (Blainville, 1830) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites obtusata (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites profundicella (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites quoyi (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites seychellensis (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites sulfurea (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1857) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Favites virens (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Goniastraea seychellensis (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Goniastrea seychellensis (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786 · unaccepted > superseded combination (basionym)
Prionastraea abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Prionastraea crassior Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea fuscoviridis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea gibbosa Klunzinger, 1879 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea magnifica (Blainville, 1830) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea obtusata (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea profundicella Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea quoyi Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea seychellensis Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea sulfurea (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastraea virens (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) · unaccepted > superseded combination
Prionastrea crassior (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea fuscoviridis (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea gibbosa (Klunzinger, 1879) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea magnifica (Blainville, 1830) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea obtusata Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea profundicella (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea quoyi (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea robusta (Dana, 1846) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea seychellensis (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
Prionastrea sulfurea Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849 · unaccepted > junior subjective synonym
- Variety Favites abdita var. fuscovirides (Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Favites abdita var. magnifica (Blainville, 1830) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Favites abdita var. profundicella (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Favites abdita var. quoyi (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Favites abdita var. robusta (Dana, 1846) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
- Variety Favites abdita var. virens (Dana, 1846) accepted as Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786) (unaccepted > junior subjective synonym)
marine, fresh, terrestrial
recent + fossil
(of Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786) Ellis, J.; Solander, D. (1786). The Natural History of many curious and uncommon Zoophytes, collected from various parts of the Globe. Systematically arranged and described by the late Daniel Solander. 4.(Benjamin White & Son: London): 1-206, pls 1-63., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/41943909 [details] 
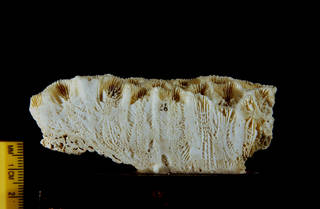
Description Colonies are massive, either rounded or hillocky. Walls are thick, calices are 7-12 mm in diameter, septa are straight,...
Description Colonies are massive, either rounded or hillocky. Walls are thick, calices are 7-12 mm in diameter, septa are straight, with prominent teeth. Colour: dark in turbid environments, other wise pale brown with green oral discs. Abundance: common and occupies a wide range of habitats with colonies frequently exceeding 1 m in diameter. (Veron, 1986).
Grows into large, rounded domes >l m in diameter. Corallites 7-14 mm across, cerioid, i.e. they share common walls, unlike Favia-though differentiating between these two genera in the field can be difficult. Colour: variable, ranging from greyish-green to reddish-brown, and has green oral discs. The fine septo-costal structure is evident when the polyps are contracted. Habitat: sheltered reefs (Richmond, 1997).
Also distributed in Australia in Kalk (1958).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Grows into large, rounded domes >l m in diameter. Corallites 7-14 mm across, cerioid, i.e. they share common walls, unlike Favia-though differentiating between these two genera in the field can be difficult. Colour: variable, ranging from greyish-green to reddish-brown, and has green oral discs. The fine septo-costal structure is evident when the polyps are contracted. Habitat: sheltered reefs (Richmond, 1997).
Also distributed in Australia in Kalk (1958).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Hoeksema, B. W.; Cairns, S. (2024). World List of Scleractinia. Favites abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=207449 on 2024-11-21
Date
action
by
2000-09-13 07:19:12Z
changed
Garcia, Maria
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 License
original description
(of Favites astrinus Link, 1807) Link, D. H. F. (1806-1808). Beschreibung der Naturalien-Sammlung der Universität zu Rostock. Adlers Erben. 1, pp. 1-50 [1806]; 2, pp. 51-100 [1807]; 3, pp. 101-165 [1807]; 4, pp. 1-30 [1807]; 5, pp. 1-38 [1808]; 6, pp. 1-38 [1808]., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/43301237 [details]
original description (of Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786) Ellis, J.; Solander, D. (1786). The Natural History of many curious and uncommon Zoophytes, collected from various parts of the Globe. Systematically arranged and described by the late Daniel Solander. 4.(Benjamin White & Son: London): 1-206, pls 1-63., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/41943909 [details]
original description (of Astraea virens Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm
page(s): 205, 228-229 [details]
original description (of Astraea robusta Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm
page(s): 206, 248-249 [details]
original description (of Prionastrea obtusata Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea quoyi Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea profundicella Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea seychellensis Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea crassior Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea gibbosa Klunzinger, 1879) Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 3. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Zweiter Abschnitt: Die Asteraeaceen und Fungiaceen. 1-100, pls. 1-10. Gutmann, Berlin. [details]
original description (of Astraea magnifica Blainville, 1830) Blainville, D. de. (1816-1830). Dictionnaire des Sciences naturelles. <em>Art. Planaire in Tom. 41. Paris 1826. p. 204-218. Art. Vers in Tom. 57. Paris 1828. p 530, 577-579. Planches, 2 partie: Règne organisé, Zoologie, Vers et Zoophytes. Paris 1816 to 1830. tab 40.</em> [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) filicosa Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) virens Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) robusta Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Prionastrea sulfurea Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Astrea fuscoviridis Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) Quoy, J. R. C.; Gaimard, J. P. (1832-1835). <i>Voyage de la corvette l'Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829, sous le commandement de M. J. Dumont d'Urville. Zoologie.</i> 1: i-l, 1-264; 2(1): 1-321 [1832]; 2(2): 321-686 [1833]; 3(1): 1-366 [1834]; 3(2): 367-954 [1835]; 4 [1833]; Atlas (Mollusques): pls 1-93 [1833] ...etc. In: Dumont d'Urville, J.; 1834, Voyage de Découvertes de l'Astrolabe. Paris, J. Tastu, Éditeur-Imprimeur., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.2132 [details]
context source (HKRMS) Chan, A. L. K.; Chan, K. K.; Choi, C. L. S.; McCorry, D.; Lee, M. W.; Ang, P. (2005). Field guide to hard corals of Hong Kong. <em>Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department, The Hong Kong SAR Government.</em> [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Veron JEN. (1986). Corals of Australia and the Indo-Pacific. <em>Angus & Robertson Publishers.</em> [details]
additional source Sheppard CRC. (1987). Coral species of the Indian Ocean and adjacent seas: a synonymised compilation and some regional distribution patterns. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 307: 1-32., available online at http:// https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00775630.307.1 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Pichon M, Wijsman-Best M. (1977). Scleractinia of Eastern Australia – Part II. Families Faviidae, Trachyphylliidae. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph series.</em> 3: 1-233. [details]
additional source Dunn, D.F., 1970. Some observations on marine life at Pulau Aur, Johore. Malay. Nat. J. 23 : 158-167.
page(s): 162 [details]
additional source Hoffmeister, J.E. (1925). Some corals from America Samoa and the Fiji Islands. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 22: 1-90, pls. 1-23.
page(s): 8, 9, 11, 12, 24-25 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1918). Some shallow-water corals from Murray Island (Australia), Cocos-Keeling Island, and Fanning Island. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 9 (213): 49-234, pls. 20-93. [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (1999). Appendix: List of extant stony corals. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 459: 13-46.
page(s): 29 [details]
additional source Randall RH. (2003). An annotated checklist of hydrozoan and scleractinian corals collected from Guam and other Mariana Islands. <em>Micronesica.</em> 35-36: 121-137.
page(s): 133 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (2007). as a contribution to UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Veron JEN. (2000). Corals of the World. Vol. 1–3. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science and CRR, Queensland, Australia.</em> [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1955). Recent and subfossil corals of Moreton Bay, Queensland. <em>Queensland. University of Queensland Papers, Department of Geology.</em> 4 (10): 1-18, pls. 1-3.
page(s): 5, 6, 13, 18, Plate 2, Fig. 1 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1961). Notes on Indo-Pacific scleractinian corals. Part 3, A new reef coral from New Caledonia. <em>Pacific Science.</em> 15: 189-191.
page(s): 189 [details]
additional source Scheer G, Pillai CSG. (1974). Report on Scleractinia from the Nicobar Islands. <em>Zoologica, Stuttgart.</em> 42(122): 1-75.
page(s): 9, 48, 74 [details]
additional source Umbgrove JHF. (1940). Madreporaria from the Togian Reefs (Gulf of Tomini, North-Celebes. <em>Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden.</em> 22: 265-310.
page(s): 267, 268, 270, 279 [details]
additional source Umbgrove JHF. (1939). Madreporaria from the Bay of Batavia. <em>Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden.</em> 22: 1-64.
page(s): 17, 28 [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T, Eguchi M. (1936). Recent reef-building corals from Japan and the South Sea Islands under the Japanese mandate. I. <em>The Science reports of the Tôhoku Imperial University, Sendai, 2nd Series (Geologie).</em> Special Volume 1: 1-66, pls. 1-59.
page(s): 3, 31-32, Pl. XXII [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T. (1935). Revised list of the reef-corals from the Japanese seas and of the fossil reef corals of the raised reefs and the Ryukyu limestone of Japan. <em>Journal of the Geological Society of Japan.</em> 42: 379-403.
page(s): 381, 384, 386, 388, 394 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG, Scheer G (1976) Report on the stony corals from the Maldive Archipelago. Results of the Xarifa Expedition 1957/58. Zoologica, Stuttgart 43 (126): 1-83, pls. 1-32. [details]
additional source Crossland C (1952) Madreporaria, Hydrocorallinae, Heliopora and Tubipora. Scientific Report Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-29 VI(3): 85-257.
page(s): 91, 140, 141 [details]
additional source Faure, G.; Pichon, M. (1978). Description de <i>Favites peresi</i>, nouvelle espèce de Scleractiniaire hermatipique de l'Océan Indien (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia). Bull. Mus. Natl. Hist. Nat., Zool. 352(513): 107-127 (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 107, 111, 113, 114, 115 [details]
additional source Wijsman-Best M (1976) Biological results of the Snellius expedition: XXVII. Faviidae collected by the Snellius Expedition. II. The genera Favites, Goniastrea, Platygyra, Oulophyllia, Leptoria, Hydnophora and Caulastrea. Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden 50: 45-63. [details]
additional source Chevalier JP (1971) Les Scléractiniaires de la Mélanésie Française (Nouvelle-Caledonie, Iles Chesterfield, Iles Loyauté, Nouvelles Hébrides). I. Expedition Française sur les Récifs Coralliens Nouv.-Calédonie 5: 1-307, pls. 1-38. Paris. [details]
additional source Wijsman-Best M (1972) Systematics and ecology of New Caledonian Faviinae (Coelenterata–Scleractinia). Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde 42: 3-90. [details]
additional source Nemenzo F (1959) Systematic studies on Philippine shallow water scleractinians: II. Suborder Faviida. Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines 16: 73-135, pls. 1-24.
page(s): 75, 94, 95 [details]
additional source Pichon, M.; Benzoni, F. (2007). Taxonomic re-appraisal of zooxanthellate Scleractinian Corals in the Maldive Archipelago. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 1441: 21–33.
page(s): 31 [details]
additional source Huang D, Benzoni F, Fukami H, Knowlton N, Smith ND, Budd AF (2014) Taxonomic classification of the reef coral families Merulinidae, Montastraeidae, and Diploastraeidae (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 171: 277–355. [details]
additional source Faustino LA. (1927). Recent Madreporaria of the Philippine Islands. <em>Bureau of Science Manila Monograph.</em> 22: 1-310, pls. 1-100.
page(s): 12, 40, 135-136, 137 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Marsh LM. (1988). Hermatypic corals of Western Australia : records and annotated species list. <em>Records Western Australian Museum Supplement.</em> 29: 1-136., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.60555
page(s): 28, 101 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1972). Stony corals of the seas around India. <em>Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Corals and Coral Reefs, 1969. Marine Biological Association of India Symposium.</em> 5: 191-216.
page(s): 206 [details]
additional source Utinomi, H. (1965). A revised catalogue of scleractinian corals from the southwest coast of Shikoku in the collections of the Ehime University and the Ehime Prefectural Museum, Matsuyama. <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 13(3): 243-261., available online at https://doi.org/10.5134/175404
page(s): 251 [details]
additional source Boshoff, P.H. (1981). An annotated checklist of Southern Africa Scleractinia. <em>Oceanographic Research Institute Investigational Report, Durban.</em> 49: 1-45.
page(s): 30 [details]
additional source Randall RH, Myers RF. (1983). The corals. Guide to the Coastal Resources of Guam: Vol. 2. <em>University of Guam Press, Guam, pp. 128.</em> [details]
additional source Khalil HM, Fathy MS, Al Sawy SM. (2021). Quaternary corals (Scleractinia: Merulinidae) from the Egyptian and Saudi Arabian Red Sea Coast. <em>Geological Journal.</em> , available online at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/gj.4145?af=R [details]
additional source Veron, J. E. N. (2000). Corals of the World, Volume III: Families Mussidae, Faviidae, Trachyphylliidae, Poritidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science. Townsville., volume 3, pp. 490.
page(s): 146-147 [details]
additional source Ryland, J. S. (1981). Reefs of southwest Viti Levu and their tourism potential. Proceedings of the Fourth International Coral Reef Symposium, 1, 293-298
page(s): 296-297 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E.; Molina, M.; Kenyon, J. (2004). Palmyra Atoll coral data compiled from Townsend Cromwell 2000-2002, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 2000-2001, and Sette 2004 surveys [Table 8]. UNPUBLISHED, UNPUBLISHED [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1954). Recent corals of the Marshall Islands: Bikini and nearby atolls, part 2, oceanography (biologic). <em>U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper.</em> 260(I): 385-486.
page(s): 393, 397, 459-460 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1983). Structure and generic diversity of recent Scleractinia of India. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India.</em> 25, 1-2, 78-90.
page(s): 87 [details]
additional source Sheppard, C. R. C. (1985). Fringing reefs in the southern region, Jeddah to Jizan. Fauna of Saudi Arabia, 7, 37-58
page(s): 45 [details]
additional source Kühlmann, D. H. H. (2006). Die Steinkorallensammlung im Naturhistorischen Museum in Rudolstadt (Thüringen) nebst ökologischen Bemerkungen. Rudolstädter Naturhistorische Schriften, 13, 37-113
page(s): 63, 91, 111 [details]
additional source Wallace, C. C.; Fellegara, I.; Muir, P. R.; Harrison, P. L. (2009). The scleractinian corals of Moreton Bay, eastern Australia: high latitude, marginal assemblages with increasing species richness. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum, 54, 2
page(s): 2, 10, 14, 66, 68, 70 [details]
original description (of Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786) Ellis, J.; Solander, D. (1786). The Natural History of many curious and uncommon Zoophytes, collected from various parts of the Globe. Systematically arranged and described by the late Daniel Solander. 4.(Benjamin White & Son: London): 1-206, pls 1-63., available online at https://www.biodiversitylibrary.org/page/41943909 [details]
original description (of Astraea virens Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm
page(s): 205, 228-229 [details]
original description (of Astraea robusta Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm
page(s): 206, 248-249 [details]
original description (of Prionastrea obtusata Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea quoyi Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea profundicella Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea seychellensis Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea crassior Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Prionastraea gibbosa Klunzinger, 1879) Klunzinger CB. (1879). Die Korallthiere des Rothen Meeres, 3. Theil: Die Steinkorallen. Zweiter Abschnitt: Die Asteraeaceen und Fungiaceen. 1-100, pls. 1-10. Gutmann, Berlin. [details]
original description (of Astraea magnifica Blainville, 1830) Blainville, D. de. (1816-1830). Dictionnaire des Sciences naturelles. <em>Art. Planaire in Tom. 41. Paris 1826. p. 204-218. Art. Vers in Tom. 57. Paris 1828. p 530, 577-579. Planches, 2 partie: Règne organisé, Zoologie, Vers et Zoophytes. Paris 1816 to 1830. tab 40.</em> [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) filicosa Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) virens Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Astraea (Fissicella) robusta Dana, 1846) Dana, J.D. (1846-1849). Zoophytes. United States Exploring Expedition during the years 1838-1842. <em>Lea and Blanchard, Philadelphia.</em> 7: 1-740, 61 pls. (1846: 1-120, 709-720; 1848: 121-708, 721-740; 1849: atlas pls. 1-61)., available online at http://www.sil.si.edu/digitalcollections/usexex/navigation/ScientificText/USExEx19_08select.cfm [details]
original description (of Prionastrea sulfurea Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849) Milne Edwards H, Haime J. (1849). Recherches sur les polypiers. Mémoire 4. Monographie des Astréides (1) (suite). <em>Annales des Sciences Naturelles, Zoologie, Series 3.</em> 12, 3, 95-197. [details]
original description (of Astrea fuscoviridis Quoy & Gaimard, 1833) Quoy, J. R. C.; Gaimard, J. P. (1832-1835). <i>Voyage de la corvette l'Astrolabe: exécuté par ordre du roi, pendant les années 1826-1827-1828-1829, sous le commandement de M. J. Dumont d'Urville. Zoologie.</i> 1: i-l, 1-264; 2(1): 1-321 [1832]; 2(2): 321-686 [1833]; 3(1): 1-366 [1834]; 3(2): 367-954 [1835]; 4 [1833]; Atlas (Mollusques): pls 1-93 [1833] ...etc. In: Dumont d'Urville, J.; 1834, Voyage de Découvertes de l'Astrolabe. Paris, J. Tastu, Éditeur-Imprimeur., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.2132 [details]
context source (HKRMS) Chan, A. L. K.; Chan, K. K.; Choi, C. L. S.; McCorry, D.; Lee, M. W.; Ang, P. (2005). Field guide to hard corals of Hong Kong. <em>Agriculture, Fisheries and Conservation Department, The Hong Kong SAR Government.</em> [details]
context source (Hexacorallia) Fautin, Daphne G. (2013). Hexacorallians of the World. (look up in IMIS) [details]
basis of record Veron JEN. (1986). Corals of Australia and the Indo-Pacific. <em>Angus & Robertson Publishers.</em> [details]
additional source Sheppard CRC. (1987). Coral species of the Indian Ocean and adjacent seas: a synonymised compilation and some regional distribution patterns. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 307: 1-32., available online at http:// https://doi.org/10.5479/si.00775630.307.1 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Pichon M, Wijsman-Best M. (1977). Scleractinia of Eastern Australia – Part II. Families Faviidae, Trachyphylliidae. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science Monograph series.</em> 3: 1-233. [details]
additional source Dunn, D.F., 1970. Some observations on marine life at Pulau Aur, Johore. Malay. Nat. J. 23 : 158-167.
page(s): 162 [details]
additional source Hoffmeister, J.E. (1925). Some corals from America Samoa and the Fiji Islands. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 22: 1-90, pls. 1-23.
page(s): 8, 9, 11, 12, 24-25 [details]
additional source Vaughan TW. (1918). Some shallow-water corals from Murray Island (Australia), Cocos-Keeling Island, and Fanning Island. <em>Papers from the Department of Marine Biology of the Carnegie Institution of Washington.</em> 9 (213): 49-234, pls. 20-93. [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (1999). Appendix: List of extant stony corals. <em>Atoll Research Bulletin.</em> 459: 13-46.
page(s): 29 [details]
additional source Randall RH. (2003). An annotated checklist of hydrozoan and scleractinian corals collected from Guam and other Mariana Islands. <em>Micronesica.</em> 35-36: 121-137.
page(s): 133 [details]
additional source Cairns, S.D., B.W. Hoeksema & J. van der Land. (2007). as a contribution to UNESCO-IOC Register of Marine Organisms. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Veron JEN. (2000). Corals of the World. Vol. 1–3. <em>Australian Institute of Marine Science and CRR, Queensland, Australia.</em> [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1955). Recent and subfossil corals of Moreton Bay, Queensland. <em>Queensland. University of Queensland Papers, Department of Geology.</em> 4 (10): 1-18, pls. 1-3.
page(s): 5, 6, 13, 18, Plate 2, Fig. 1 [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1961). Notes on Indo-Pacific scleractinian corals. Part 3, A new reef coral from New Caledonia. <em>Pacific Science.</em> 15: 189-191.
page(s): 189 [details]
additional source Scheer G, Pillai CSG. (1974). Report on Scleractinia from the Nicobar Islands. <em>Zoologica, Stuttgart.</em> 42(122): 1-75.
page(s): 9, 48, 74 [details]
additional source Umbgrove JHF. (1940). Madreporaria from the Togian Reefs (Gulf of Tomini, North-Celebes. <em>Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden.</em> 22: 265-310.
page(s): 267, 268, 270, 279 [details]
additional source Umbgrove JHF. (1939). Madreporaria from the Bay of Batavia. <em>Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden.</em> 22: 1-64.
page(s): 17, 28 [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T, Eguchi M. (1936). Recent reef-building corals from Japan and the South Sea Islands under the Japanese mandate. I. <em>The Science reports of the Tôhoku Imperial University, Sendai, 2nd Series (Geologie).</em> Special Volume 1: 1-66, pls. 1-59.
page(s): 3, 31-32, Pl. XXII [details]
additional source Yabe H, Sugiyama T. (1935). Revised list of the reef-corals from the Japanese seas and of the fossil reef corals of the raised reefs and the Ryukyu limestone of Japan. <em>Journal of the Geological Society of Japan.</em> 42: 379-403.
page(s): 381, 384, 386, 388, 394 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG, Scheer G (1976) Report on the stony corals from the Maldive Archipelago. Results of the Xarifa Expedition 1957/58. Zoologica, Stuttgart 43 (126): 1-83, pls. 1-32. [details]
additional source Crossland C (1952) Madreporaria, Hydrocorallinae, Heliopora and Tubipora. Scientific Report Great Barrier Reef Expedition 1928-29 VI(3): 85-257.
page(s): 91, 140, 141 [details]
additional source Faure, G.; Pichon, M. (1978). Description de <i>Favites peresi</i>, nouvelle espèce de Scleractiniaire hermatipique de l'Océan Indien (Cnidaria, Anthozoa, Scleractinia). Bull. Mus. Natl. Hist. Nat., Zool. 352(513): 107-127 (look up in IMIS)
page(s): 107, 111, 113, 114, 115 [details]
additional source Wijsman-Best M (1976) Biological results of the Snellius expedition: XXVII. Faviidae collected by the Snellius Expedition. II. The genera Favites, Goniastrea, Platygyra, Oulophyllia, Leptoria, Hydnophora and Caulastrea. Zoologische Mededelingen, Leiden 50: 45-63. [details]
additional source Chevalier JP (1971) Les Scléractiniaires de la Mélanésie Française (Nouvelle-Caledonie, Iles Chesterfield, Iles Loyauté, Nouvelles Hébrides). I. Expedition Française sur les Récifs Coralliens Nouv.-Calédonie 5: 1-307, pls. 1-38. Paris. [details]
additional source Wijsman-Best M (1972) Systematics and ecology of New Caledonian Faviinae (Coelenterata–Scleractinia). Bijdragen tot de Dierkunde 42: 3-90. [details]
additional source Nemenzo F (1959) Systematic studies on Philippine shallow water scleractinians: II. Suborder Faviida. Natural and Applied Science Bulletin, University of the Philippines 16: 73-135, pls. 1-24.
page(s): 75, 94, 95 [details]
additional source Pichon, M.; Benzoni, F. (2007). Taxonomic re-appraisal of zooxanthellate Scleractinian Corals in the Maldive Archipelago. <em>Zootaxa.</em> 1441: 21–33.
page(s): 31 [details]
additional source Huang D, Benzoni F, Fukami H, Knowlton N, Smith ND, Budd AF (2014) Taxonomic classification of the reef coral families Merulinidae, Montastraeidae, and Diploastraeidae (Cnidaria: Anthozoa: Scleractinia). Zoological Journal of the Linnean Society 171: 277–355. [details]
additional source Faustino LA. (1927). Recent Madreporaria of the Philippine Islands. <em>Bureau of Science Manila Monograph.</em> 22: 1-310, pls. 1-100.
page(s): 12, 40, 135-136, 137 [details]
additional source Veron JEN, Marsh LM. (1988). Hermatypic corals of Western Australia : records and annotated species list. <em>Records Western Australian Museum Supplement.</em> 29: 1-136., available online at https://doi.org/10.5962/bhl.title.60555
page(s): 28, 101 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1972). Stony corals of the seas around India. <em>Proceedings of the First International Symposium on Corals and Coral Reefs, 1969. Marine Biological Association of India Symposium.</em> 5: 191-216.
page(s): 206 [details]
additional source Utinomi, H. (1965). A revised catalogue of scleractinian corals from the southwest coast of Shikoku in the collections of the Ehime University and the Ehime Prefectural Museum, Matsuyama. <em>Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory.</em> 13(3): 243-261., available online at https://doi.org/10.5134/175404
page(s): 251 [details]
additional source Boshoff, P.H. (1981). An annotated checklist of Southern Africa Scleractinia. <em>Oceanographic Research Institute Investigational Report, Durban.</em> 49: 1-45.
page(s): 30 [details]
additional source Randall RH, Myers RF. (1983). The corals. Guide to the Coastal Resources of Guam: Vol. 2. <em>University of Guam Press, Guam, pp. 128.</em> [details]
additional source Khalil HM, Fathy MS, Al Sawy SM. (2021). Quaternary corals (Scleractinia: Merulinidae) from the Egyptian and Saudi Arabian Red Sea Coast. <em>Geological Journal.</em> , available online at https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/gj.4145?af=R [details]
additional source Veron, J. E. N. (2000). Corals of the World, Volume III: Families Mussidae, Faviidae, Trachyphylliidae, Poritidae. Australian Institute of Marine Science. Townsville., volume 3, pp. 490.
page(s): 146-147 [details]
additional source Ryland, J. S. (1981). Reefs of southwest Viti Levu and their tourism potential. Proceedings of the Fourth International Coral Reef Symposium, 1, 293-298
page(s): 296-297 [details]
additional source Maragos, J. E.; Molina, M.; Kenyon, J. (2004). Palmyra Atoll coral data compiled from Townsend Cromwell 2000-2002, U.S. Fish and Wildlife Service 2000-2001, and Sette 2004 surveys [Table 8]. UNPUBLISHED, UNPUBLISHED [details]
additional source Wells JW. (1954). Recent corals of the Marshall Islands: Bikini and nearby atolls, part 2, oceanography (biologic). <em>U.S. Geological Survey Professional Paper.</em> 260(I): 385-486.
page(s): 393, 397, 459-460 [details]
additional source Pillai CSG. (1983). Structure and generic diversity of recent Scleractinia of India. <em>Journal of the Marine Biological Association of India.</em> 25, 1-2, 78-90.
page(s): 87 [details]
additional source Sheppard, C. R. C. (1985). Fringing reefs in the southern region, Jeddah to Jizan. Fauna of Saudi Arabia, 7, 37-58
page(s): 45 [details]
additional source Kühlmann, D. H. H. (2006). Die Steinkorallensammlung im Naturhistorischen Museum in Rudolstadt (Thüringen) nebst ökologischen Bemerkungen. Rudolstädter Naturhistorische Schriften, 13, 37-113
page(s): 63, 91, 111 [details]
additional source Wallace, C. C.; Fellegara, I.; Muir, P. R.; Harrison, P. L. (2009). The scleractinian corals of Moreton Bay, eastern Australia: high latitude, marginal assemblages with increasing species richness. Memoirs of the Queensland Museum, 54, 2
page(s): 2, 10, 14, 66, 68, 70 [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 36992, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 38746, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 39321, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 40803, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 48643, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 50725, geounit Micronesian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 50779, geounit Micronesian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 53031, geounit Palau Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Favites virens (Dana, 1846)) IGPS 56639, geounit Palau Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Prionastraea robusta (Dana, 1846)) BMNH, geounit Chinese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype (of Prionastraea obtusata (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849)) BMNH, geounit Vietnamese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype HLD X2: 127-47, geounit Indian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype HLD X2: 151-6, geounit Indian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype HLD X2: 156-9, geounit Indian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 38581, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 38750, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 39261, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 40802, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 44981, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 45104, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 45113, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 47398, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 47847, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 47848, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 48642, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 48644, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 48747, geounit Japanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 48747, geounit Marshall Islands Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 49212, geounit Taiwanese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 49217, geounit Chinese Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 53059, geounit Marshall Islands Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 53236, geounit Palau Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype IGPS 56636, geounit Palau Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype NMSR 8627, geounit Yemeni Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 106-58, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 107-58, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 112-73, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 125-74, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 152-73, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 18-72, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 18-73, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 205-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 206-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 207-74, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 207-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 208-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 209-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 215-74, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 219-74, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 246-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 26-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 270-77, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 270-78, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 271-77, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 272-77, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 292-77, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 297-77, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 298-78, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 298-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 302-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 303-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 335-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 347-79, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 364-80, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 425-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 509-78, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 509-78, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 53-59, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 584-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 585-84, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 606-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 6-59, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 6-73, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 761-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 859-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 862-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 891-81, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Nontype WAM 90-85, geounit Australian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Goniastraea seychellensis (Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849)) MZUS, geounit Mauritian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Prionastraea gibbosa Klunzinger, 1879) MZUS, geounit Mauritian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Prionastraea magnifica (Blainville, 1830)) MZUS, geounit Philippines Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786)) IMC mrt-25, geounit Myanmar Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786)) IMC, geounit Indian Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786)) IMC, geounit Myanmar Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
Unknown type (of Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786)) IMC, geounit Myanmar Exclusive Economic Zone [details]
From editor or global species database
Biology zooxanthellate [details]Unreviewed
Description Colonies are massive, either rounded or hillocky. Walls are thick, calices are 7-12 mm in diameter, septa are straight, with prominent teeth. Colour: dark in turbid environments, other wise pale brown with green oral discs. Abundance: common and occupies a wide range of habitats with colonies frequently exceeding 1 m in diameter. (Veron, 1986).Grows into large, rounded domes >l m in diameter. Corallites 7-14 mm across, cerioid, i.e. they share common walls, unlike Favia-though differentiating between these two genera in the field can be difficult. Colour: variable, ranging from greyish-green to reddish-brown, and has green oral discs. The fine septo-costal structure is evident when the polyps are contracted. Habitat: sheltered reefs (Richmond, 1997).
Also distributed in Australia in Kalk (1958).
Tropical Indo-Pacific in Kalk (1958). [details]
Remark Original combination in Sheppard (1998). Type locality: unrecorded (Veron, 1986). [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| English | larger star coral | [details] |
| Japanese | カメノコキクメイシオオカメノコキクメイシ [from synonym] | [details] |
To Barcode of Life (12 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (11 publications) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (26 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications) (from synonym Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Favia hemprichii (Ehrenberg, 1834))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Prionastrea obtusata Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Favites abdita)
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins) (from synonym Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786)
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins)
To IUCN Red List (Least Concern)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE26closeup) (from synonym Astraea virens Dana, 1846)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE63verycloseup) (from synonym Astraea robusta Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Astraea robusta Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Astraea virens Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (84 records)
To ITIS
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (11 publications) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (26 publications)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (5 publications) (from synonym Favia abdita (Ellis & Solander, 1786))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Favia hemprichii (Ehrenberg, 1834))
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (8 publications) (from synonym Prionastrea obtusata Milne Edwards & Haime, 1849)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Favites abdita)
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins) (from synonym Favites virens (Dana, 1846))
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins) (from synonym Madrepora abdita Ellis & Solander, 1786)
To GenBank (63 nucleotides; 45 proteins)
To IUCN Red List (Least Concern)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE26closeup) (from synonym Astraea virens Dana, 1846)
To NMNH Extant Collection (IZCOE63verycloseup) (from synonym Astraea robusta Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Astraea robusta Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (1 record) (from synonym Astraea virens Dana, 1846)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Cnidaria Collection (84 records)
To ITIS