WoRMS taxon details
Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake & Kominami ex Oda) Gert Hansen & Moestrup, 2000
233024 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:233024)
accepted
Species
Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935 · unaccepted (synonym)
Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985 · unaccepted (synonym)
Gyrodinium nagasakiense Takayama & Adachi, 1984 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine
(of Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935) Oda M. 1935. The red tide of <i>Gymnodinium mikimotoi</i> n.sp. (MS.) and the effect of altering copper sulphate to prevent the growth of it. Dobutsugaku Zasshi, Zoological Society of Japan 47 (555): 35-48. [details]
Type locality contained in Gokasho Bay
type locality contained in Gokasho Bay [details]
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:50158
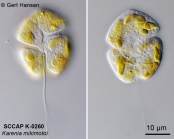
Description Cell size: 18–37 μm long, 14–35 μm wide, broadly oval and very dorso-ventrally flattened. ‘Small’ and ‘big’...
status Until very recently this species has been confused with the non-toxic species Gymnodinium aureolum (syn.: Gyrodinium aureolum).
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:50158 [details]
Description Cell size: 18–37 μm long, 14–35 μm wide, broadly oval and very dorso-ventrally flattened. ‘Small’ and ‘big’...
Description Cell size: 18–37 μm long, 14–35 μm wide, broadly oval and very dorso-ventrally flattened. ‘Small’ and ‘big’ cells occurring at the same time. Epicone sub-hemispherical to broadly conical, hypocone slightly bilobed. Cingulum slightly pre-median and displaced 1/9 to 1/4 of the cell length. Sulcus slightly invading epicone and widening toward the antapex. Ten to twenty chloroplasts, brown-yellow in colour are scattered to the cell periphery. Nucleus ellipsoidal to reniform, located in the hypocone left lobe. Apical groove thick, extending 1/3 down the dorsal side of the epicone (Fukuyo et al., 1990). In 1965 during toxic blooms in Japan Karenia mikimotoi was first called Gymnodinium type ‘65’. It was later renamed Gymnodinium nagasakiense until the genus Karenia was erected (Hansen et al., 2000; Partensky et al., 1988; Takayama and Adachi, 1984). From Lassus et al. 2016. [details]
status Until very recently this species has been confused with the non-toxic species Gymnodinium aureolum (syn.: Gyrodinium aureolum).
status Until very recently this species has been confused with the non-toxic species Gymnodinium aureolum (syn.: Gyrodinium aureolum). [details]
Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway (taxonomic information republished from AlgaeBase with permission of M.D. Guiry). Karenia mikimotoi (Miyake & Kominami ex Oda) Gert Hansen & Moestrup, 2000. Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=233024 on 2025-04-18
Date
action
by
2006-07-26 06:43:45Z
created
Camba Reu, Cibran
2015-06-26 12:00:51Z
changed
db_admin
2019-07-16 06:31:19Z
changed
db_admin
Copyright notice: the information originating from AlgaeBase may not be downloaded or replicated by any means, without the written permission of the copyright owner (generally AlgaeBase). Fair usage of data in scientific publications is permitted.
Nomenclature
original description
(of Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935) Oda M. 1935. The red tide of <i>Gymnodinium mikimotoi</i> n.sp. (MS.) and the effect of altering copper sulphate to prevent the growth of it. Dobutsugaku Zasshi, Zoological Society of Japan 47 (555): 35-48. [details]
original description (of Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985) Takayama H. & Adachi R. 1984. <i>Gymnodinium nagasakiense</i> sp. nov., a red-tide forming dinophyte in the adjacent waters of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 31: 7-14. [details]
basis of record Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
new combination reference Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, G.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, O. (2000). Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. <em>Phycologia.</em> 39(4): 302-317., available online at https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-302.1 [details]
original description (of Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985) Takayama H. & Adachi R. 1984. <i>Gymnodinium nagasakiense</i> sp. nov., a red-tide forming dinophyte in the adjacent waters of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 31: 7-14. [details]
basis of record Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
new combination reference Daugbjerg, N.; Hansen, G.; Larsen, J.; Moestrup, O. (2000). Phylogeny of some of the major genera of dinoflagellates based on ultrastructure and partial LSU rDNA sequence data, including the erection of three new genera of unarmoured dinoflagellates. <em>Phycologia.</em> 39(4): 302-317., available online at https://doi.org/10.2216/i0031-8884-39-4-302.1 [details]
Taxonomy
taxonomy source
Hansen, G., Daugbjerg, N. & Henriksen, P. (2000). Comparative study of <i>Gymnodinium mikimotoi</i> and <i>Gymnodinium aureolum</i>, comb. nov. (=<i>Gyrodinium aureolum</i>) based on morphology, pigment composition, and molecular data. J. of Phycol. 36: 394-410. [details]
source of synonymy Takayama H. & Adachi R. 1984. <i>Gymnodinium nagasakiense</i> sp. nov., a red-tide forming dinophyte in the adjacent waters of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 31: 7-14. [details]
source of synonymy Takayama H. & Adachi R. 1984. <i>Gymnodinium nagasakiense</i> sp. nov., a red-tide forming dinophyte in the adjacent waters of Japan. Bull. Plankton Soc. Jap. 31: 7-14. [details]
Ecology
ecology source
Leles, S. G.; Mitra, A.; Flynn, K. J.; Tillmann, U.; Stoecker, D.; Jeong, H. J.; Burkholder, J.; Hansen, P. J.; Caron, D. A.; Glibert, P. M.; Hallegraeff, G.; Raven, J. A.; Sanders, R. W.; Zubkov, M. (2019). Sampling bias misrepresents the biogeographical significance of constitutive mixotrophs across global oceans. <em>Global Ecology and Biogeography.</em> 28(4): 418-428., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/geb.12853 [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
ecology source Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Song, J.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M. (2011). Will harmful dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi grow phagotrophically?. <em>Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology.</em> 29(4), 849-859. [details]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
ecology source Zhang, Q.; Yu, R.; Song, J.; Yan, T.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, M. (2011). Will harmful dinoflagellate Karenia mikimotoi grow phagotrophically?. <em>Chinese Journal of Oceanology and Limnology.</em> 29(4), 849-859. [details]
ecology source Mitra, A.; Caron, D. A.; Faure, E.; Flynn, K. J.; Leles, S. G.; Hansen, P. J.; McManus, G. B.; Not, F.; Do Rosario Gomes, H.; Santoferrara, L. F.; Stoecker, D. K.; Tillmann, U. (2023). The Mixoplankton Database (MDB): Diversity of photo‐phago‐trophic plankton in form, function, and distribution across the global ocean. <em>Journal of Eukaryotic Microbiology.</em> 70(4)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/jeu.12972 [details]
Other
context source (Introduced species)
Katsanevakis, S.; Bogucarskis, K.; Gatto, F.; Vandekerkhove, J.; Deriu, I.; Cardoso A.S. (2012). Building the European Alien Species Information Network (EASIN): a novel approach for the exploration of distributed alien species data. <em>BioInvasions Records.</em> 1: 235-245., available online at http://easin.jrc.ec.europa.eu [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
context source (HKRMS) Hodgkiss, I. J.; Chan, B. S. S. (1987). Phytoplankton dynamics in Tolo Harbour. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Asian Marine Biology 4.Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 103-112. [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., E. Meric, M. Verlaque, P. Galli, C.F. Boudouresque, A. Giangrande, M. Cinar & M. Bilecenoglu. (2008). Additions to the annotated list of marine alien biota in the Mediterranean with special emphasis on Foraminifera and Parasites. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 9(1): 119-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.146 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Tangen K. 1977. Blooms of <i>Gyrodinium aureolum</i> (Dinophyceae) in North European waters, accompanied by mortality in marine organisms. Sarsia 63: 123-133. [details]
additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
toxicology source Gentien P. & Arzul G. 1990. Exotoxin production by <i>Gyrodinium</i> cf. <i>aureolum</i> (Dinophyceae). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 70: 571-581. [details]
toxicology source Satake, M., Shoji, M., Oshima, Y., Naoki, H., Fujita, T. & Yasumoto, T. (2002). Gymnocin-A, a cytotoxic polyether from the noxious red tide dinoflagellate, <i>Gymnodinium mikimotoi</i>. <em>Tetrahedr. Lett.</em> 43: 5829-5832. [details]
context source (HKRMS) Hodgkiss, I. J.; Chan, B. S. S. (1987). Phytoplankton dynamics in Tolo Harbour. <em>In: Morton B, editor. Asian Marine Biology 4.Hong Kong University Press, Hong Kong.</em> 103-112. [details]
context source (Schelde) Maris, T., O. Beauchard, S. Van Damme, E. Van den Bergh, S. Wijnhoven & P. Meire. (2013). Referentiematrices en Ecotoopoppervlaktes Annex bij de Evaluatiemethodiek Schelde-estuarium Studie naar “Ecotoopoppervlaktes en intactness index”. [Reference matrices and Ecotope areas Annex to the Evaluation methodology Scheldt estuary Study on “Ecotope areas and intactness index”. <em>Monitor Taskforce Publication Series, 2013-01. NIOZ: Yerseke.</em> 35 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details]
additional source Guiry, M.D. & Guiry, G.M. (2025). AlgaeBase. <em>World-wide electronic publication, National University of Ireland, Galway.</em> searched on YYYY-MM-DD., available online at http://www.algaebase.org [details]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Chang, F.H.; Charleston, W.A.G.; McKenna, P.B.; Clowes, C.D.; Wilson, G.J.; Broady, P.A. (2012). Phylum Myzozoa: dinoflagellates, perkinsids, ellobiopsids, sporozoans, in: Gordon, D.P. (Ed.) (2012). New Zealand inventory of biodiversity: 3. Kingdoms Bacteria, Protozoa, Chromista, Plantae, Fungi. pp. 175-216. [details]
additional source Zenetos, A., E. Meric, M. Verlaque, P. Galli, C.F. Boudouresque, A. Giangrande, M. Cinar & M. Bilecenoglu. (2008). Additions to the annotated list of marine alien biota in the Mediterranean with special emphasis on Foraminifera and Parasites. <em>Mediterranean Marine Science.</em> 9(1): 119-165., available online at https://doi.org/10.12681/mms.146 [details] Available for editors
additional source Tangen K. 1977. Blooms of <i>Gyrodinium aureolum</i> (Dinophyceae) in North European waters, accompanied by mortality in marine organisms. Sarsia 63: 123-133. [details]
additional source Steidinger, K. A., M. A. Faust, and D. U. Hernández-Becerril. 2009. Dinoflagellates (Dinoflagellata) of the Gulf of Mexico, Pp. 131–154 in Felder, D.L. and D.K. Camp (eds.), Gulf of Mexico–Origins, Waters, and Biota. Biodiversity. Texas A&M Press, College [details]
additional source Moestrup, Ø., Akselman, R., Cronberg, G., Elbraechter, M., Fraga, S., Halim, Y., Hansen, G., Hoppenrath, M., Larsen, J., Lundholm, N., Nguyen, L. N., Zingone, A. (Eds) (2009 onwards). IOC-UNESCO Taxonomic Reference List of Harmful Micro Algae., available online at http://www.marinespecies.org/HAB [details]
toxicology source Gentien P. & Arzul G. 1990. Exotoxin production by <i>Gyrodinium</i> cf. <i>aureolum</i> (Dinophyceae). J. Mar. Biol. Ass. U.K. 70: 571-581. [details]
toxicology source Satake, M., Shoji, M., Oshima, Y., Naoki, H., Fujita, T. & Yasumoto, T. (2002). Gymnocin-A, a cytotoxic polyether from the noxious red tide dinoflagellate, <i>Gymnodinium mikimotoi</i>. <em>Tetrahedr. Lett.</em> 43: 5829-5832. [details]
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
From editor or global species database
LSID urn:lsid:algaebase.org:taxname:50158 [details]From regional or thematic species database
Description Cell size: 18–37 μm long, 14–35 μm wide, broadly oval and very dorso-ventrally flattened. ‘Small’ and ‘big’ cells occurring at the same time. Epicone sub-hemispherical to broadly conical, hypocone slightly bilobed. Cingulum slightly pre-median and displaced 1/9 to 1/4 of the cell length. Sulcus slightly invading epicone and widening toward the antapex. Ten to twenty chloroplasts, brown-yellow in colour are scattered to the cell periphery. Nucleus ellipsoidal to reniform, located in the hypocone left lobe. Apical groove thick, extending 1/3 down the dorsal side of the epicone (Fukuyo et al., 1990). In 1965 during toxic blooms in Japan Karenia mikimotoi was first called Gymnodinium type ‘65’. It was later renamed Gymnodinium nagasakiense until the genus Karenia was erected (Hansen et al., 2000; Partensky et al., 1988; Takayama and Adachi, 1984). From Lassus et al. 2016. [details]Harmful effect Fish and invertebrate mortality. Cytotoxic polyethers, named Gymnocin-A and Gymnocin-B, have been isolated from Japanese cultured material [details]
Introduced species impact Chinese part of the Eastern Chinese Sea(Marine Region) Other impact - undefined or uncertain (Bloom forming) [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Germany (Nation) : Shipping [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal in Norwegian part of the Skagerrak (Marine Region) : Shipping [details]
Introduced species vector dispersal Chinese part of the Eastern Chinese Sea(Marine Region) Ships: General [details]
status Until very recently this species has been confused with the non-toxic species Gymnodinium aureolum (syn.: Gyrodinium aureolum). [details]
| Language | Name | |
|---|---|---|
| Japanese | アカシオハダカオビムシ [from synonym] | [details] |
Published in AlgaeBase  (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
(from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
Published in AlgaeBase
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Gyrodinium nagasakiense Takayama & Adachi, 1984)
(from synonym Gyrodinium nagasakiense Takayama & Adachi, 1984)
Published in AlgaeBase (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
(from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To Barcode of Life (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To Barcode of Life (2 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Gymnodinium nagasakiense) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Karenia mikimotoi)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To GenBank (439 nucleotides; 360 proteins)
To GenBank (439 nucleotides; 360 proteins) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
 (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
(from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)Published in AlgaeBase

Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Gyrodinium nagasakiense Takayama & Adachi, 1984)
(from synonym Gyrodinium nagasakiense Takayama & Adachi, 1984)Published in AlgaeBase
 (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
(from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)To Barcode of Life (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To Barcode of Life (2 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (4 publications) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (7 publications) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Biological Information System for Marine Life (BISMaL) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Dyntaxa
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Gymnodinium nagasakiense) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Karenia mikimotoi)
To GenBank (1 nucleotides; 0 proteins) (from synonym Gymnodinium nagasakiense H.Takayama & M.Adachi, 1985)
To GenBank (439 nucleotides; 360 proteins)
To GenBank (439 nucleotides; 360 proteins) (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)
To Information system on Aquatic Non-Indigenous and Cryptogenic Species (AquaNIS)
To PESI
To PESI (from synonym Gymnodinium mikimotoi Miyake & Kominami ex Oda, 1935)