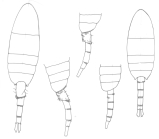
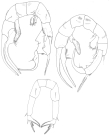
WoRMS taxon details
Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (Scott T., 1894)
355187 (urn:lsid:marinespecies.org:taxname:355187)
accepted
Species
Heterocalanus serricaudatus Scott T., 1894 · unaccepted
Pseudodiaptomus nudus Tanaka, 1960 · unaccepted (synonym)
marine, brackish, fresh, terrestrial
(of Heterocalanus serricaudatus Scott T., 1894) Scott, T. (1894). Additions to the fauna of the Firth of Forth. Part VI. <em>Report of the Fishery Board for Scotland.</em> 12(3):231-271, pls. 5-10. (look up in IMIS) [details] 
Walter, T.C.; Boxshall, G. (2025). World of Copepods Database. Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (Scott T., 1894). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species at: https://www.marinespecies.org/aphia.php?p=taxdetails&id=355187 on 2025-04-04
Date
action
by
![]() The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
The webpage text is licensed under a Creative Commons
Attribution 4.0 License
Nomenclature
original description
(of Heterocalanus serricaudatus Scott T., 1894) Scott, T. (1894). Additions to the fauna of the Firth of Forth. Part VI. <em>Report of the Fishery Board for Scotland.</em> 12(3):231-271, pls. 5-10. (look up in IMIS) [details] 
original description (of Pseudodiaptomus nudus Tanaka, 1960) Tanaka, O. (1960). The pelagic copepods of the Izu region, Middle Japan. Systematic account VI. Families Phaennidae and Tharybidae. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 8(1):85-135, figs. 81-105. (30-v-1960) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
original description (of Pseudodiaptomus nudus Tanaka, 1960) Tanaka, O. (1960). The pelagic copepods of the Izu region, Middle Japan. Systematic account VI. Families Phaennidae and Tharybidae. Publications of the Seto Marine Biological Laboratory 8(1):85-135, figs. 81-105. (30-v-1960) [details] Available for editors
Ecology
ecology source
Brun, P., M.R. Payne & T. Kiørboe. (2017). A trait database for marine copepods. <em>Earth System Science Data.</em> 9(1):99-113., available online at https://doi.org/10.5194/essd-9-99-2017 [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
Other
additional source
Ganapati, P.N., C.C. Narasimhamurti & K. Shanthakumari. (1964). A new haplosporidian parasite, Coelosporidium schmackeriae from the body cavity of a marine copepod Schmackeria serricaudata. <em>Indian Academy of Sciences.</em> 60(5):309-314. [details] Available for editors  [request]
[request]
additional source Anzeer, F.M., B. Santhosh, J. Imelda, J. Shoji, G. Gopakumar, S. Vinod, K.S. Aneesh, V.A. Mijo & C. Unnikrishnan. (2018). Biological information and culture techniques of Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (T. Scott, 1894). <em>In: Santhosh, B., M.K. Anil, F.M. Anzeer, K.S. Aneesh, V. Mijo, G.G. Abraham, R.M. George, A. Gopalakrishnan & C. Unnikrishnan (Eds.). (2018). Culture Techniques of Marine Copepods. ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Kochi, Kerala, India, St. Francis Press, Kochi. 144 pp.</em> :51-58. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Altaff, K. (2020). Feeding and Reproductive Biology of Two Potential Calanoid Copepod Species of Pseudodiaptomus for Mass Culture. <em>International Journal of Zoological Investigations.</em> 6(2):246-259. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Altaff, K. (2018). Occurrence of oviducal glands in two tropical marine calanoid copepods Pseudodiaptomus annandalei and Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus - a new report. <em>International Journal of Zoology and Applied Biosciences.</em> 3(3): 387-392. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Raval, J.V., A. Vyas, N. Chavda & S. Vyas. (2019). Comparative Zooplanktonic Diversity with Respect to Physicochemical Parameters of Saraswati and Shingoda Rivers of Gujarat, India. <em>Ambient Science.</em> 6(1):37-41., available online at https://doi.org/10.21276/ambi.2019.06.1.ra06 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Nishida, S., R. Machida & J.S. Hwang. (2024). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Copepoda, Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae) from the coastal waters of northern Taiwan with notes on co-occurring and previously recorded species. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 97(10-11):1255-1279. Sep 2024., available online at https://doi.org/10.1163/15685403-Bja10386 [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Cleve, P.T. (1905). The plankton of the South African seas. I. Copepoda. Marine Investigations in South Africa, Cape Town 3:177-210, pl.1-6.
page(s): 196 [details]
additional source Krishnaswamy, S. (1950). Larval stages of some copepods in the Madras plankton and their seasonal fluctuations. Journal of the Madras University, Series B 19:33-58, figs. 1-68, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Marques, E. (1974). Contribuiçao para o conhecimento dos Copépodes marinhos de Cabo Verde (Ilhas: Brava, Fogo, Santiago e Maio). la parte - Copepoda Calanoida. [Contribution to the knowledge of marine copepods of Cape Verde (Islands: Brava, Fogo, Santiago and Maio). the part - Copepoda Calanoida.]. <em>Garcia de Orta, Série de Zoologia, Lisbon.</em> 3(1):7-20, figs. 1-6. [Portuguese]. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Marsh, C.D. (1933). Synopsis of the calanoid crustaceans, exclusive of the Diaptomidae, found in fresh and brackish waters, chiefly of North America. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 82(18)(2959):1-58, pls. 1-24. (30-vi-1933) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Saraswathy, M. (1967). Pelagic copepods from the inshore waters off Trivandrum coast. Proceedings of the Symposium on Crustacea, Ernakulam, 12-15 January 1965. Symposium Series, Marine Biological Association of India (2)1:74-106, figs. 1-11. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Sewell, R.B.S. (1924). Crustacea Copepoda: Fauna of Chilka Lake. <em>Memoirs of the Indian Museum, Calcutta.</em> 5(12):771-851, pls. 44-59. (vii-1924). [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Ummerkutty, A.N.P. (1967). Studies on Indian copepods. 8. Observations on the diurnal vertical movements of planktonic copepods in the Gulf of Mannar. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 63(2):332-343, figs. 1-4, tabs. 1-5, map. (27-iii-1967) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Vervoort, W. (1965). Pelagic Copepoda. Part II. Copepoda Calanoida of the families Phaennidae up to and including Acartiidae, containing the description of a new species of Aetideidae. Atlantide Report, Danish Expedition to Coasts of Tropical West Africa 1945-1946 8:9-216. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Wellershaus, S. (1969). On the taxonomy of planctonic Copepoda in the Cochin Backwater (a South Indian estuary). Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven 11:245-286. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Rebello, V., J. Narvekar, P. Gadi, A. Venenkar, M. Gauns & S.P. Kumar (2014). First record of the calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (Scott, T. 1894), (Copepoda: Calanoida: Pseudodiaptomidae) in the Equatorial Indian Ocean. <i>Asian Fisheries Science</i>. 27(2):149-159. [details] Available for editors [request]
[request]
additional source Anzeer, F.M., B. Santhosh, J. Imelda, J. Shoji, G. Gopakumar, S. Vinod, K.S. Aneesh, V.A. Mijo & C. Unnikrishnan. (2018). Biological information and culture techniques of Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (T. Scott, 1894). <em>In: Santhosh, B., M.K. Anil, F.M. Anzeer, K.S. Aneesh, V. Mijo, G.G. Abraham, R.M. George, A. Gopalakrishnan & C. Unnikrishnan (Eds.). (2018). Culture Techniques of Marine Copepods. ICAR-Central Marine Fisheries Research Institute, Kochi, Kerala, India, St. Francis Press, Kochi. 144 pp.</em> :51-58. [details] Available for editors
additional source Altaff, K. (2020). Feeding and Reproductive Biology of Two Potential Calanoid Copepod Species of Pseudodiaptomus for Mass Culture. <em>International Journal of Zoological Investigations.</em> 6(2):246-259. [details] Available for editors
additional source Altaff, K. (2018). Occurrence of oviducal glands in two tropical marine calanoid copepods Pseudodiaptomus annandalei and Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus - a new report. <em>International Journal of Zoology and Applied Biosciences.</em> 3(3): 387-392. [details] Available for editors
additional source Raval, J.V., A. Vyas, N. Chavda & S. Vyas. (2019). Comparative Zooplanktonic Diversity with Respect to Physicochemical Parameters of Saraswati and Shingoda Rivers of Gujarat, India. <em>Ambient Science.</em> 6(1):37-41., available online at https://doi.org/10.21276/ambi.2019.06.1.ra06 [details] Available for editors
additional source Nishida, S., R. Machida & J.S. Hwang. (2024). A new species of Pseudodiaptomus (Copepoda, Calanoida, Pseudodiaptomidae) from the coastal waters of northern Taiwan with notes on co-occurring and previously recorded species. <em>Crustaceana.</em> 97(10-11):1255-1279. Sep 2024., available online at https://doi.org/10.1163/15685403-Bja10386 [details] Available for editors
additional source Cleve, P.T. (1905). The plankton of the South African seas. I. Copepoda. Marine Investigations in South Africa, Cape Town 3:177-210, pl.1-6.
page(s): 196 [details]
additional source Krishnaswamy, S. (1950). Larval stages of some copepods in the Madras plankton and their seasonal fluctuations. Journal of the Madras University, Series B 19:33-58, figs. 1-68, tab. 1. [details] Available for editors
additional source Marques, E. (1974). Contribuiçao para o conhecimento dos Copépodes marinhos de Cabo Verde (Ilhas: Brava, Fogo, Santiago e Maio). la parte - Copepoda Calanoida. [Contribution to the knowledge of marine copepods of Cape Verde (Islands: Brava, Fogo, Santiago and Maio). the part - Copepoda Calanoida.]. <em>Garcia de Orta, Série de Zoologia, Lisbon.</em> 3(1):7-20, figs. 1-6. [Portuguese]. [details] Available for editors
additional source Marsh, C.D. (1933). Synopsis of the calanoid crustaceans, exclusive of the Diaptomidae, found in fresh and brackish waters, chiefly of North America. Proceedings of the United States National Museum 82(18)(2959):1-58, pls. 1-24. (30-vi-1933) [details] Available for editors
additional source Saraswathy, M. (1967). Pelagic copepods from the inshore waters off Trivandrum coast. Proceedings of the Symposium on Crustacea, Ernakulam, 12-15 January 1965. Symposium Series, Marine Biological Association of India (2)1:74-106, figs. 1-11. [details] Available for editors
additional source Sewell, R.B.S. (1924). Crustacea Copepoda: Fauna of Chilka Lake. <em>Memoirs of the Indian Museum, Calcutta.</em> 5(12):771-851, pls. 44-59. (vii-1924). [details] Available for editors
additional source Ummerkutty, A.N.P. (1967). Studies on Indian copepods. 8. Observations on the diurnal vertical movements of planktonic copepods in the Gulf of Mannar. Journal of the Bombay Natural History Society 63(2):332-343, figs. 1-4, tabs. 1-5, map. (27-iii-1967) [details] Available for editors
additional source Vervoort, W. (1965). Pelagic Copepoda. Part II. Copepoda Calanoida of the families Phaennidae up to and including Acartiidae, containing the description of a new species of Aetideidae. Atlantide Report, Danish Expedition to Coasts of Tropical West Africa 1945-1946 8:9-216. [details] Available for editors
additional source Wellershaus, S. (1969). On the taxonomy of planctonic Copepoda in the Cochin Backwater (a South Indian estuary). Veröffentlichungen des Instituts für Meeresforschung in Bremerhaven 11:245-286. [details] Available for editors
additional source Liu, J.Y. [Ruiyu] (ed.). (2008). Checklist of marine biota of China seas. <em>China Science Press.</em> 1267 pp. (look up in IMIS) [details] Available for editors
additional source Rebello, V., J. Narvekar, P. Gadi, A. Venenkar, M. Gauns & S.P. Kumar (2014). First record of the calanoid copepod Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus (Scott, T. 1894), (Copepoda: Calanoida: Pseudodiaptomidae) in the Equatorial Indian Ocean. <i>Asian Fisheries Science</i>. 27(2):149-159. [details] Available for editors
 Present
Present  Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio
Present in aphia/obis/gbif/idigbio  Inaccurate
Inaccurate  Introduced: alien
Introduced: alien  Containing type locality
Containing type locality
Marine Planktonic Copepods (Banyuls/OOB/UPMC/CNRS) Note: Including taxonomic identification plates, remarks, geographic distribution, ecological information & reference list
To Barcode of Life (5 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Pseudodiaptomus nudus Tanaka, 1960)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (13 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus)
To GenBank (9 nucleotides; 6 proteins) (from synonym Heterocalanus serricaudatus Scott T., 1894)
To GenBank (9 nucleotides; 6 proteins)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (9 records)
To Barcode of Life (5 barcodes)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (1 publication) (from synonym Pseudodiaptomus nudus Tanaka, 1960)
To Biodiversity Heritage Library (13 publications)
To European Nucleotide Archive, ENA (Pseudodiaptomus serricaudatus)
To GenBank (9 nucleotides; 6 proteins) (from synonym Heterocalanus serricaudatus Scott T., 1894)
To GenBank (9 nucleotides; 6 proteins)
To USNM Invertebrate Zoology Arthropoda Collection (9 records)