Integrated Marine Information System (IMIS)
Persons | Institutes | Publications | Projects | DatasetsYoda demiankoopi Holland, Hiley & Rouse, 2022
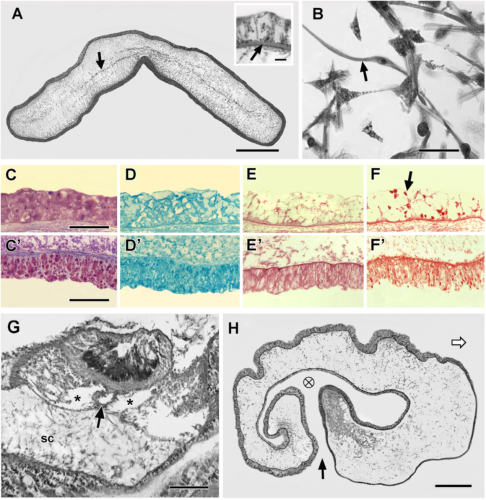
Description FIGURE 5 Yoda demiankoopi n. sp. Holotype SIO-BIC H51 (5A–F,H), paratype SIO-BIC H47 (5G). (A) Cross section near anterior end of the proboscis; arrow indicates a lamina of fibrous connective tissue. Azure A. Inset in A: enlargement of dorsal epidermis showing nuclei and basal nerve fiber layer (arrow). Hematoxylin. (B) Connective tissue of proboscis, comprising connective tissue fibers, smooth muscles (arrow), and free cells. Ponceau. (C–F) Dorsal epidermis of proboscis stained, respectively, with azure A, alcian blue, periodic acid–Schiff (PAS), and Ponceau; arrow in F indicates a local strong reaction for protein. (C0–F0 ) Ventral epidermis of proboscis stained, respectively, with azure A, alcian blue, PAS, and Ponceau. (G) Cross section of collar nerve cord (top center) overlying dorsal hemal vessel (arrow), perihemal coeloms (asterisks), and stomochord (sc). Hematoxylin. (H) Cross section of lip on right side (through x–x0 in Figure 2). White arrow shows direction of crawling, black arrow indicates opening to ciliary groove, and cross-in-circle engineering symbol indicates substrate in groove is conveyed into page. Azure A and Ponceau. Scale bars: A = 2 mm; Inset A = 50 μm; B = 25 μm; C–F, C0–F0 = 200 μm; G = 250 μm; H = 500 μm
Source: Holland, N. D.; Hiley, A. S.; Rouse, G. W. (2022). A new species of deep‐sea torquaratorid enteropneust (Hemichordata): A sequential hermaphrodite with exceptionally wide lips. Invertebrate Biology. 141(3)., available online at https://doi.org/10.1111/ivb.12379
·
Click here to return to the thumbnails overview